The Quantity Theory of Money

The Roles of Central Banks

The Objectives of Monetary Policy

The Money Creation Process

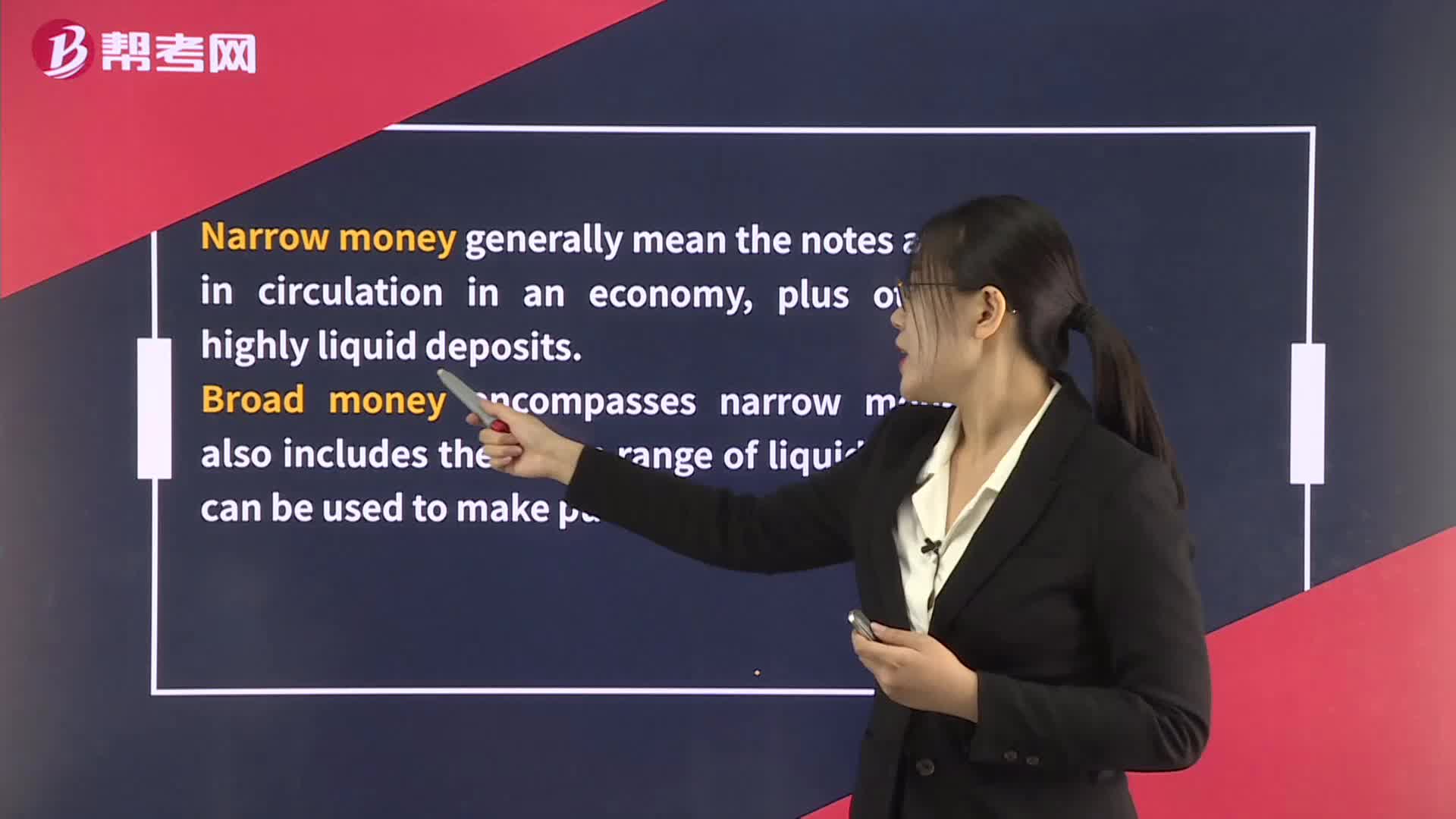
The Functions of Money

The Demand for Money

The Costs of Inflation

The Construction of Price Indexes

The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using the Different Tools of Fiscal Policy

Factors Influencing the Mix of Fiscal and Monetary Policy

Elliott Wave Theory

Theories of the Business Cycle - Neoclassical and Austrian Schools

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360