Bayes’ formula Principles of Counting

Balance of Payment Components

The Objectives of Monetary Policy

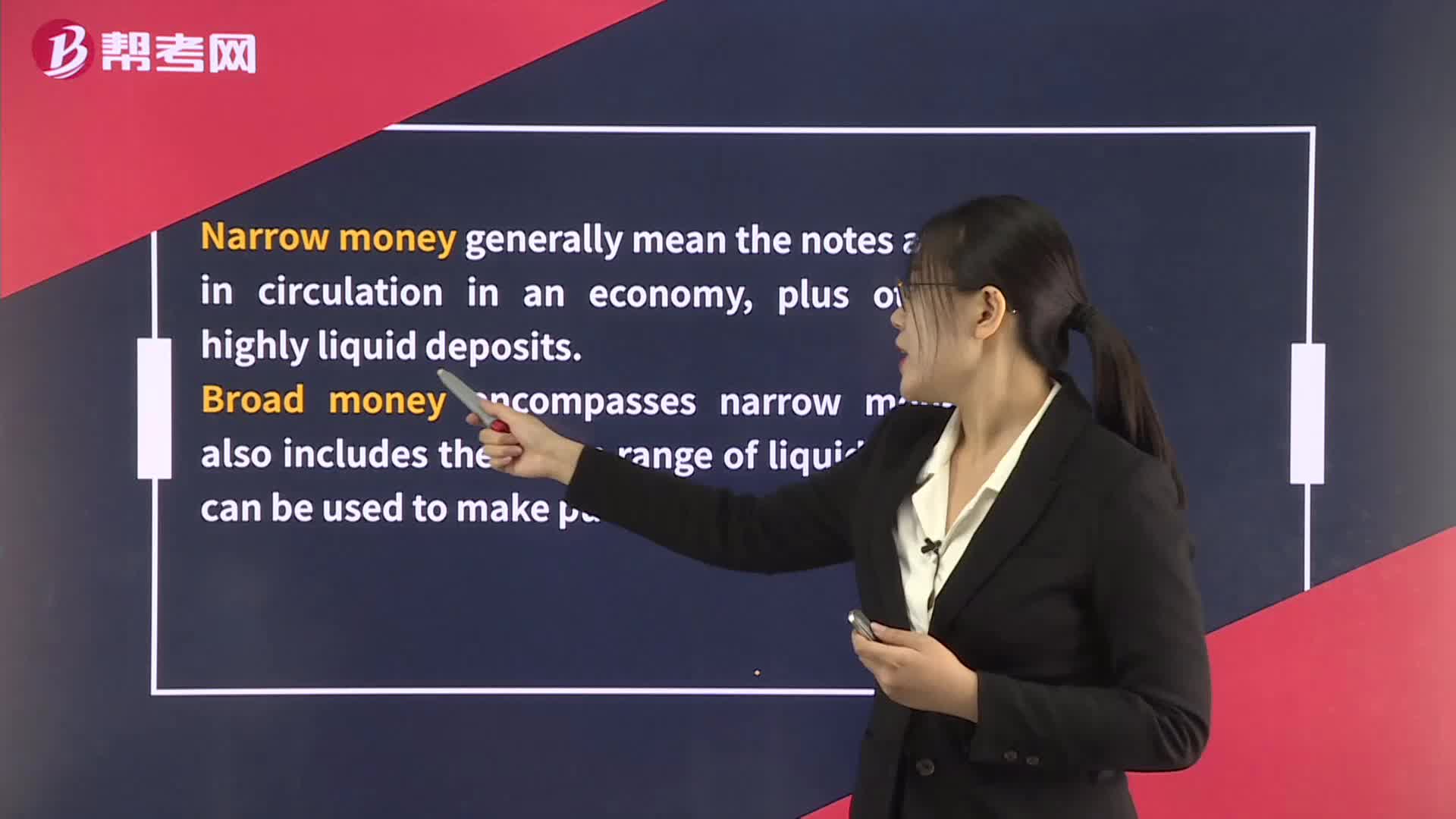
The Functions of Money

Examination of a Company’s Financial Position

Examination of a Company’s Performance

Identification of Market Structure – HHI

Identification of Market Structure – Concentration Ratio

Identification of Market Structure – Econometric Method

The Costs of Inflation

The Construction of Price Indexes

The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using the Different Tools of Fiscal Policy

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360