Type I and Type II Errors in Hypothesis Testing

Definition of Alternative Hypothesis

Hypothesis Testing
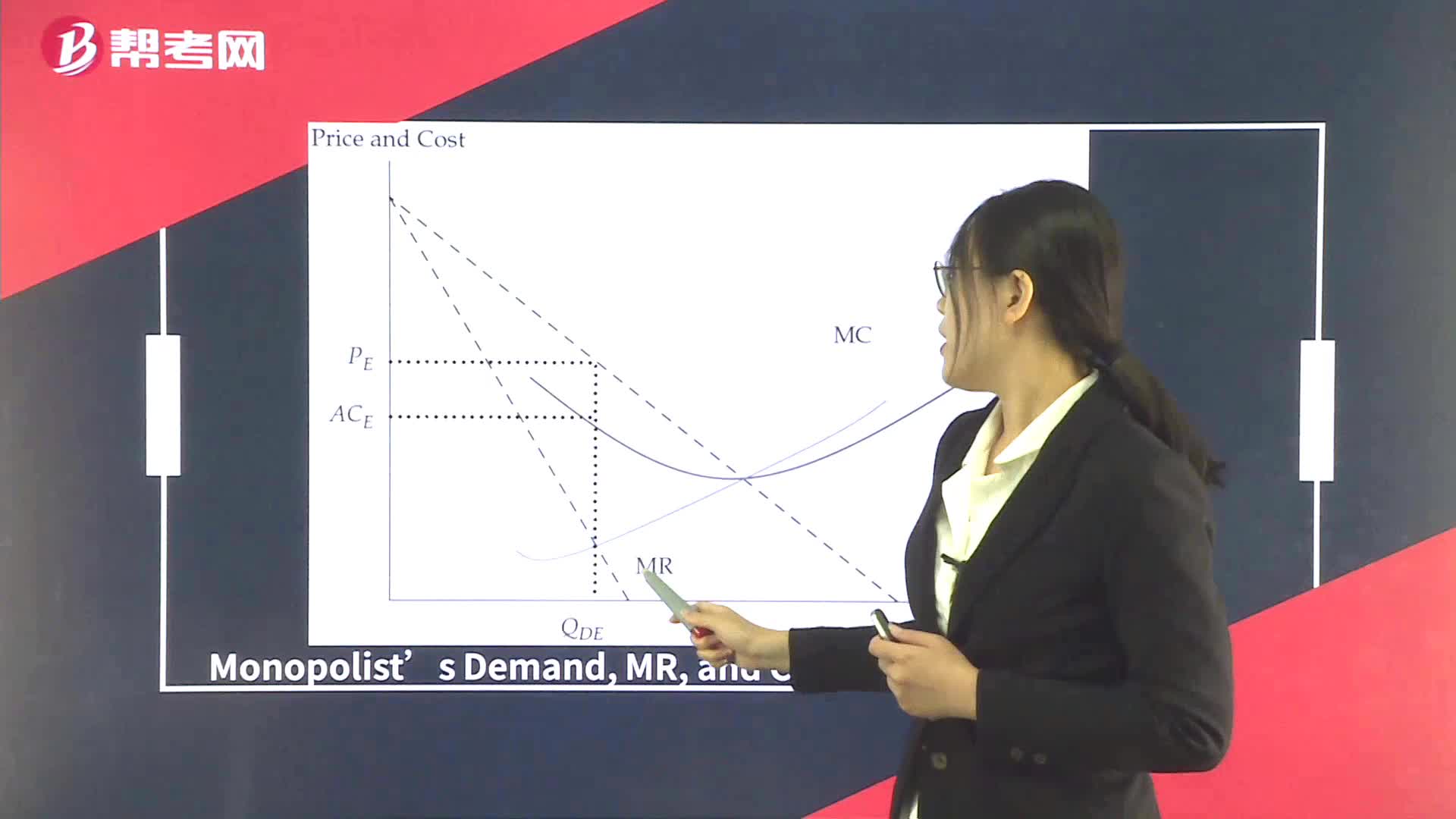
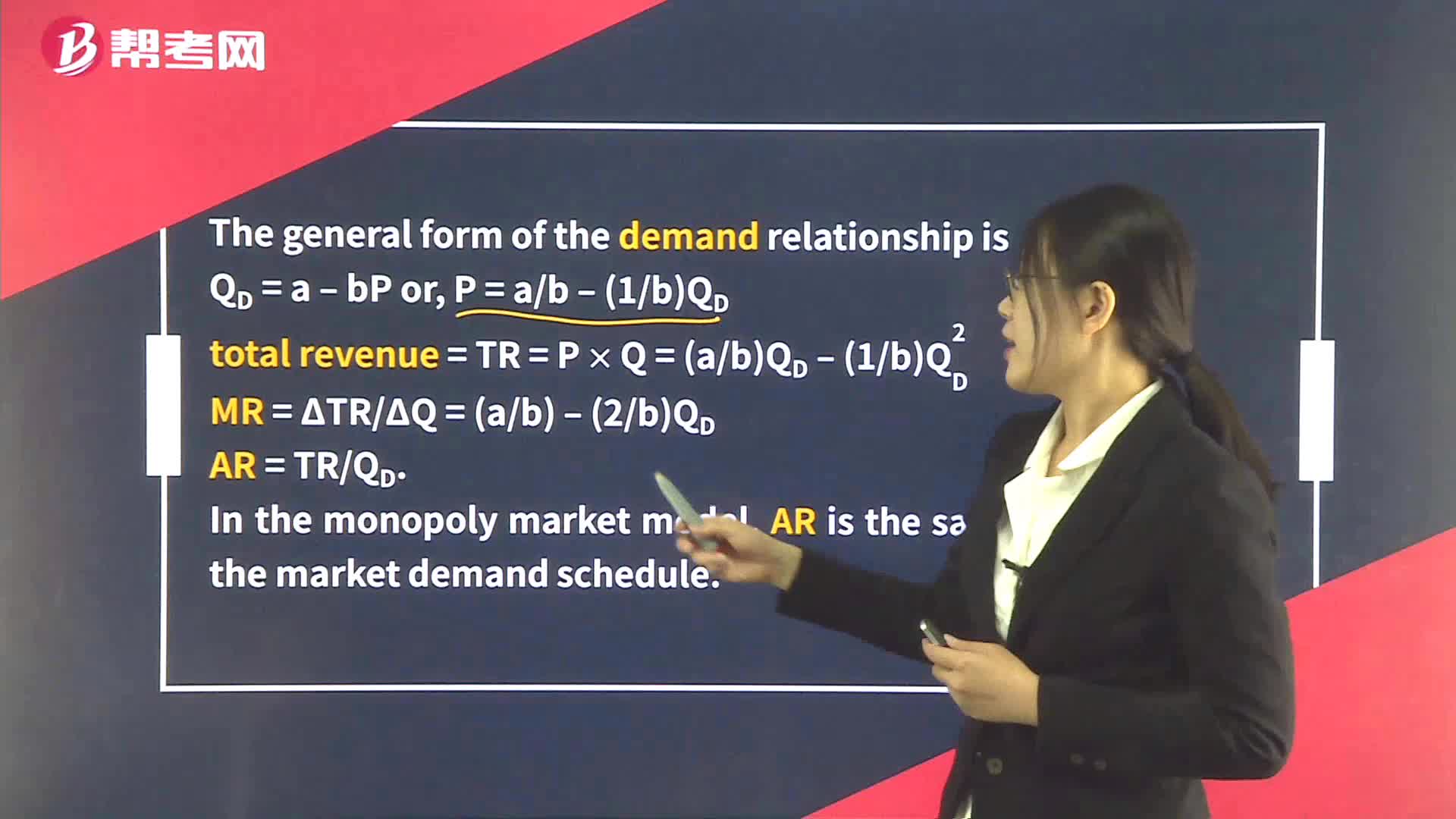
Supply Analysis in Monopoly

Total, Variable, Fixed, and Marginal Cost and Output
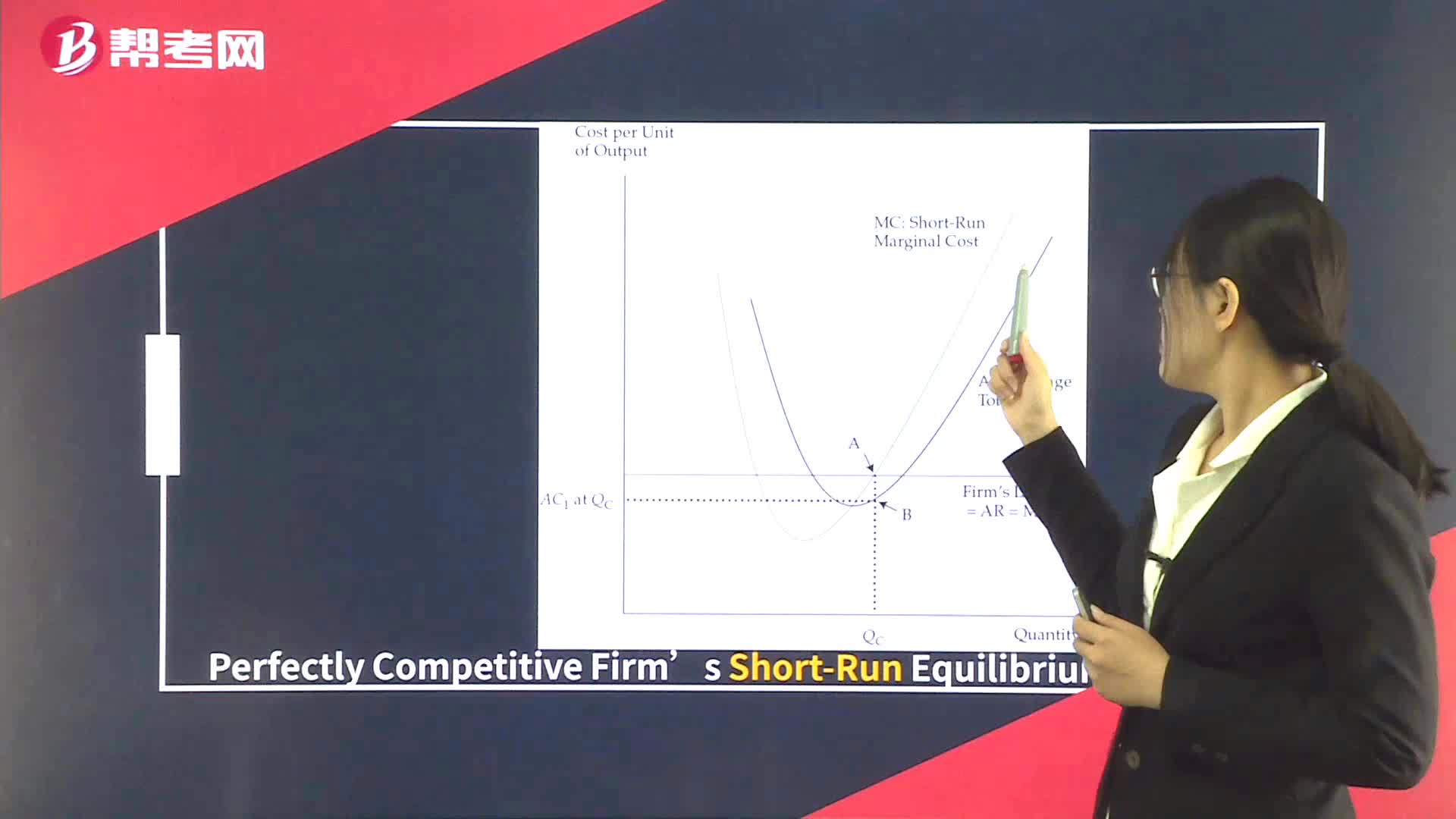
Optimal Price and Output in Perfect Competition

Hypothesis Tests Concerning Variance

Hypothesis Tests Concerning the Mean

Shifts in the AD and AS curves and Equilibriums

Shifts in Aggregate Supply

Long-Run Equilibrium in Oligopoly Market

Shifts in Aggregate Demand

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360