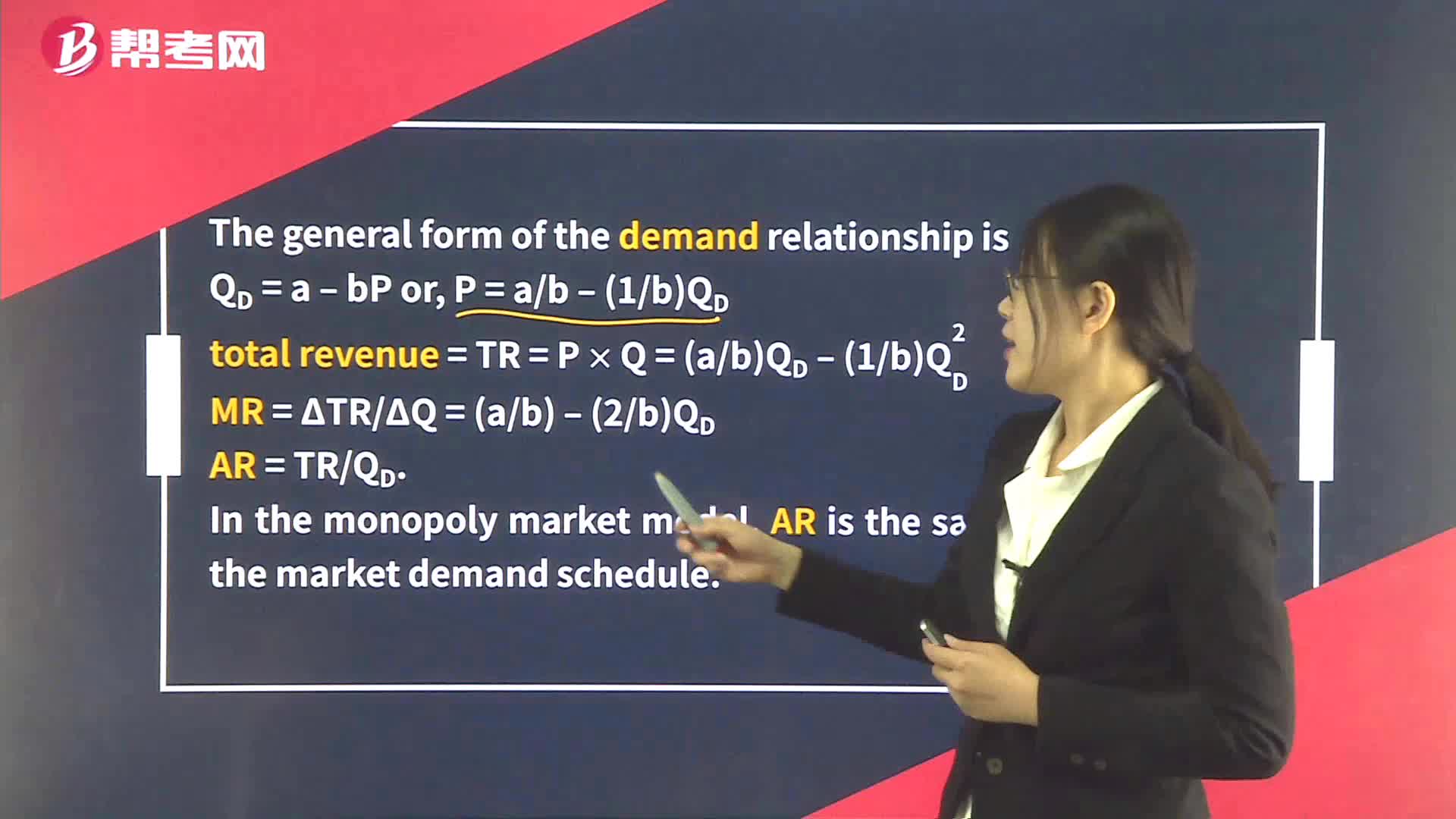
Shifts in Aggregate Demand
Aggregate demand refers to the total demand for goods and services in an economy. It is affected by various factors such as changes in consumer spending, investment, government spending, and net exports. Shifts in aggregate demand occur when there is a change in any of these factors.
1. Consumer Spending: Consumer spending is the largest component of aggregate demand. Any change in consumer behavior can lead to a shift in aggregate demand. For example, if consumers become more confident about the economy and their future income, they may increase their spending. This will increase aggregate demand, shifting the AD curve to the right. On the other hand, if consumers become more cautious and cut back on spending, aggregate demand will decrease, shifting the AD curve to the left.
2. Investment: Investment refers to spending on capital goods such as machinery, equipment, and buildings. A change in investment spending can also lead to a shift in aggregate demand. For example, if businesses become more optimistic about the future and decide to invest more, aggregate demand will increase, shifting the AD curve to the right. Conversely, if businesses become more pessimistic and cut back on investment, aggregate demand will decrease, shifting the AD curve to the left.
3. Government Spending: Government spending is another component of aggregate demand. A change in government spending can also lead to a shift in aggregate demand. For example, if the government increases spending on infrastructure projects, aggregate demand will increase, shifting the AD curve to the right. Conversely, if the government cuts spending on social programs, aggregate demand will decrease, shifting the AD curve to the left.
4. Net Exports: Net exports refer to the difference between a country's exports and imports. A change in net exports can also lead to a shift in aggregate demand. For example, if a country's exports increase, aggregate demand will increase, shifting the AD curve to the right. Conversely, if a country's imports increase, aggregate demand will decrease, shifting the AD curve to the left.
Overall, shifts in aggregate demand can have significant effects on an economy. They can lead to changes in output, employment, and prices. Policymakers often use monetary and fiscal policies to manage aggregate demand and stabilize the economy.
 帮考网校
帮考网校