
下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失
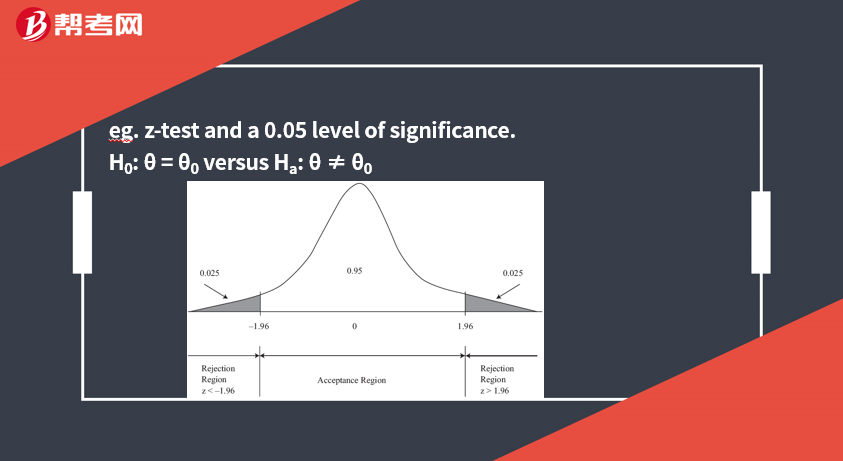
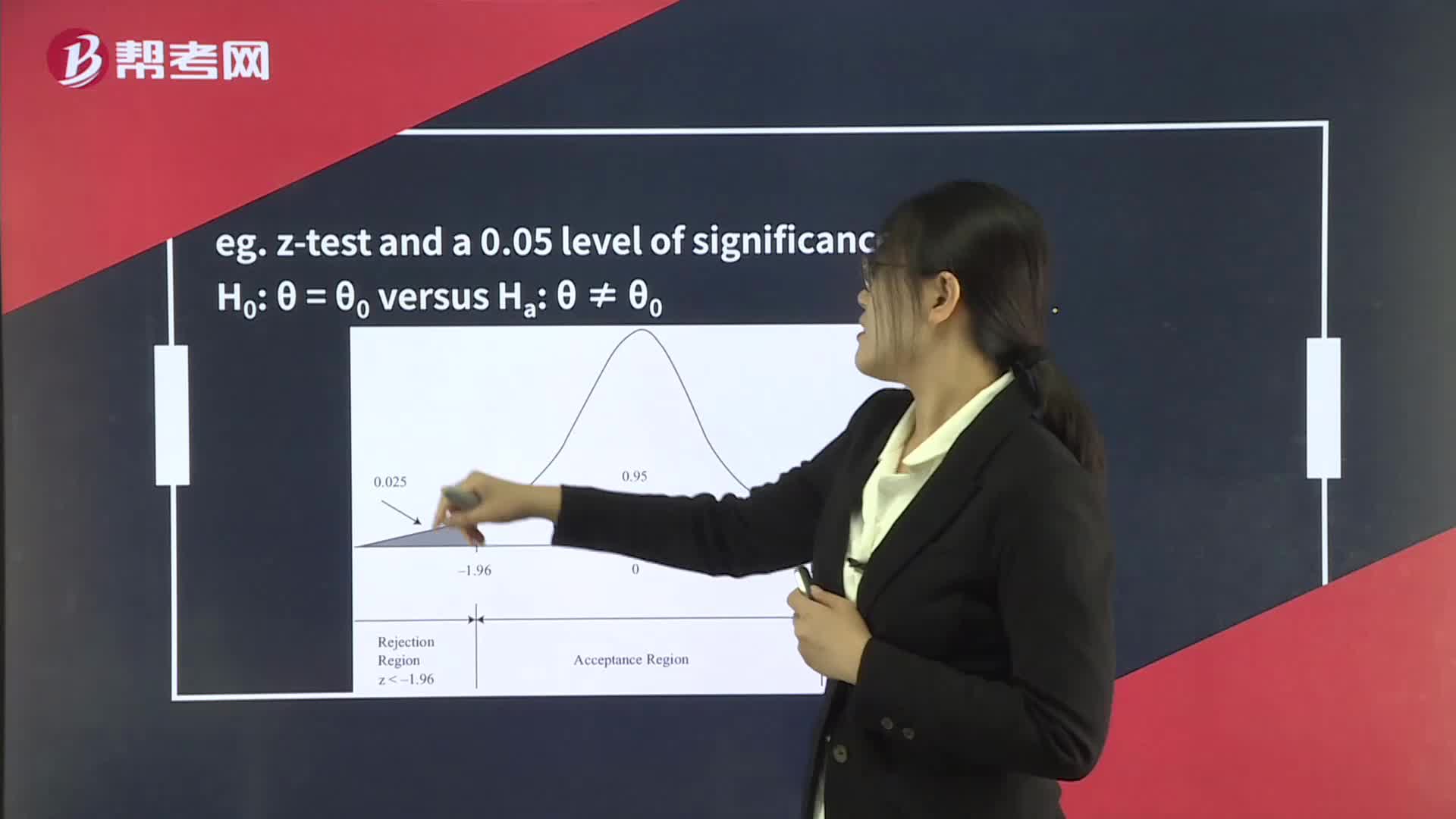
Rejection Point (Critical Value) for the Test Statistic
A rejection point (critical value) for a test statistic is a value with which the computed test statistic is compared to decide whether to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
20200807103444105.jpg)
[Practice Problems] An investment consultant conducts two independent random samples of 5-year performance data for US and European absolute return hedge funds. The consultant decides to test whether the two means are statistically different from one another at a 0.05 level of significance. The two populations are assumed to be normally distributed with unknown but equal variances.
20200807103454553.jpg)
20200807103505989.jpg)
[Solutions] A
The t-statistic value of 0.4893 does not fall into the critical value rejection regions (≤ –1.984 or > 1.984). Instead it falls well within the acceptance region. Thus, H0 cannot be rejected; the result is not statistically significant at the 0.05 level.
 680
680Confidence Intervals for the Population Mean:error,A confidence:Unknown.normal.Population Variance Unknown—t-Distribution.of freedom for tα2 is n − 1
 300
300Rejection Point (Critical Value) for the Test Statistic:the result is not statistically significant at the 0.05 level.
 87
87Test Statistic:Test,Statistic. A test statistic is a quantity:whose value is the basis for deciding whether or not to;testthe F-distribution for an F-test.

微信扫码关注公众号
获取更多考试热门资料