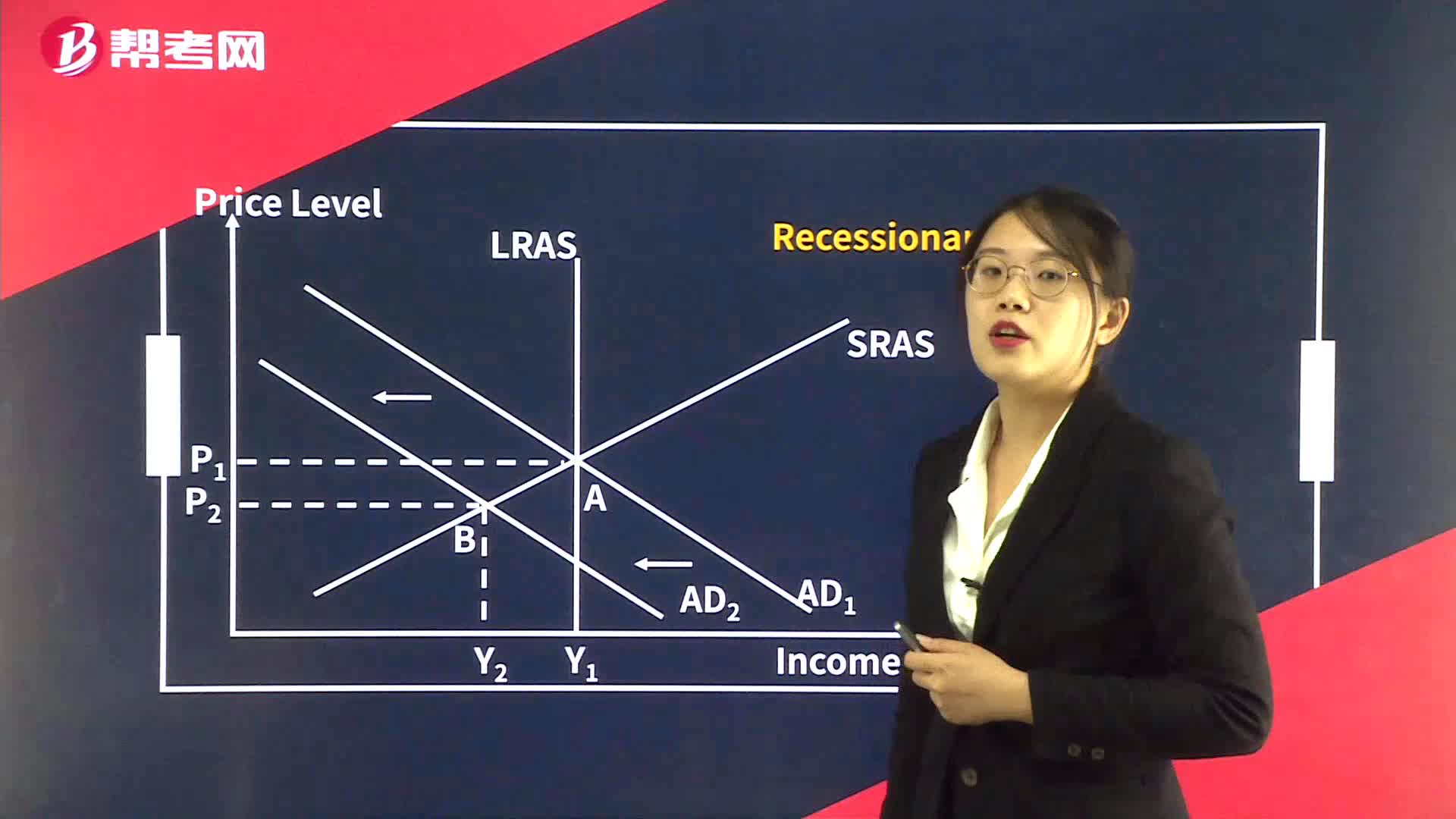
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Recessionary Gap
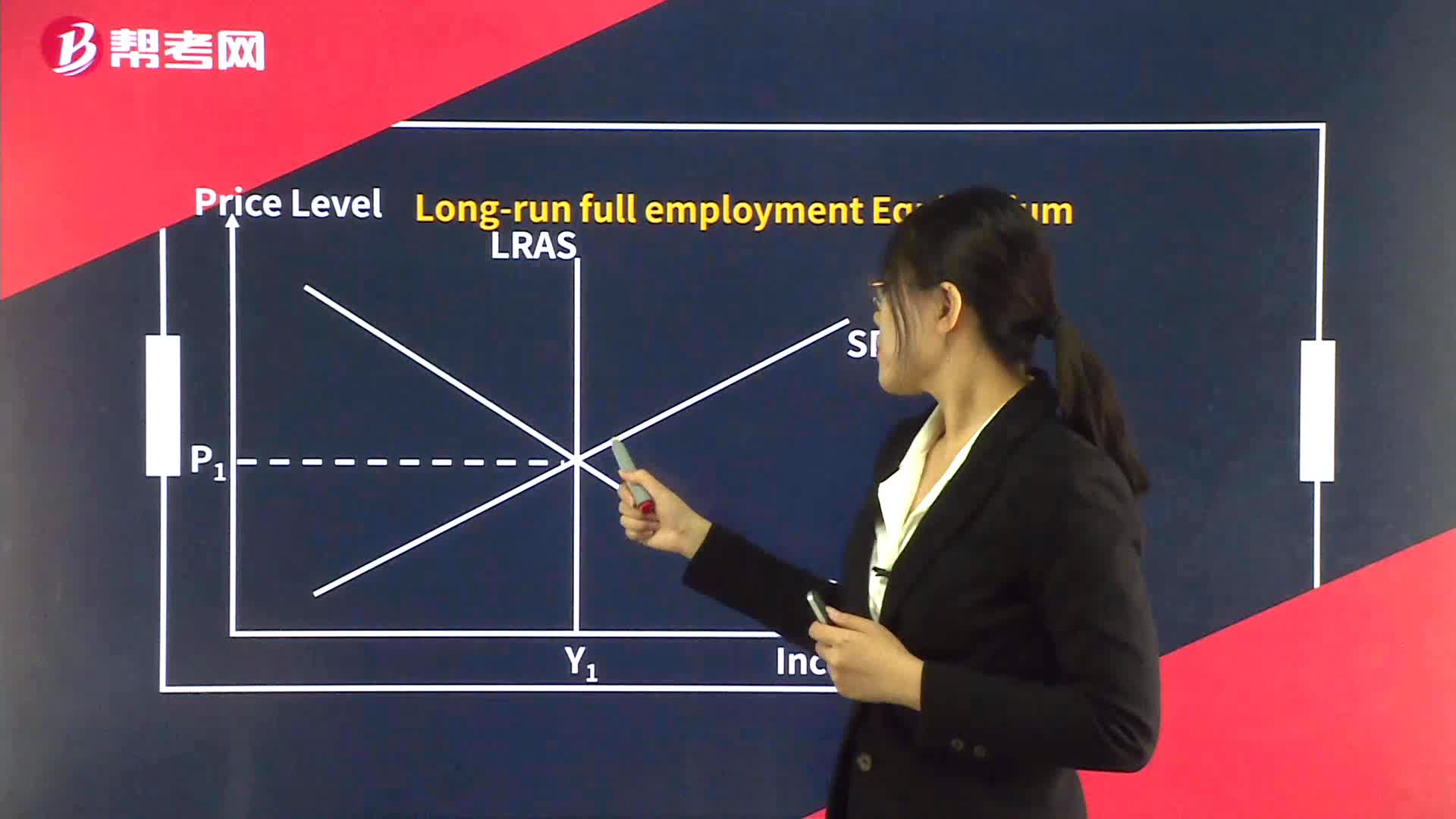
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Long-Run Equilibrium

Price Indexes and Their Usage

Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Inflationary Gap

Deficits and the Fiscal Stance

Overall Payroll Employment and Productivity Indicators

Calculation of GDP – Income Approach

The Production Function and Potential GDP

Portfolio Expected Return and Variance of Return

Calculation of GDP – Expenditure Approach

Monetary and Fiscal Policy

Economic Growth and Sustainability

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360













