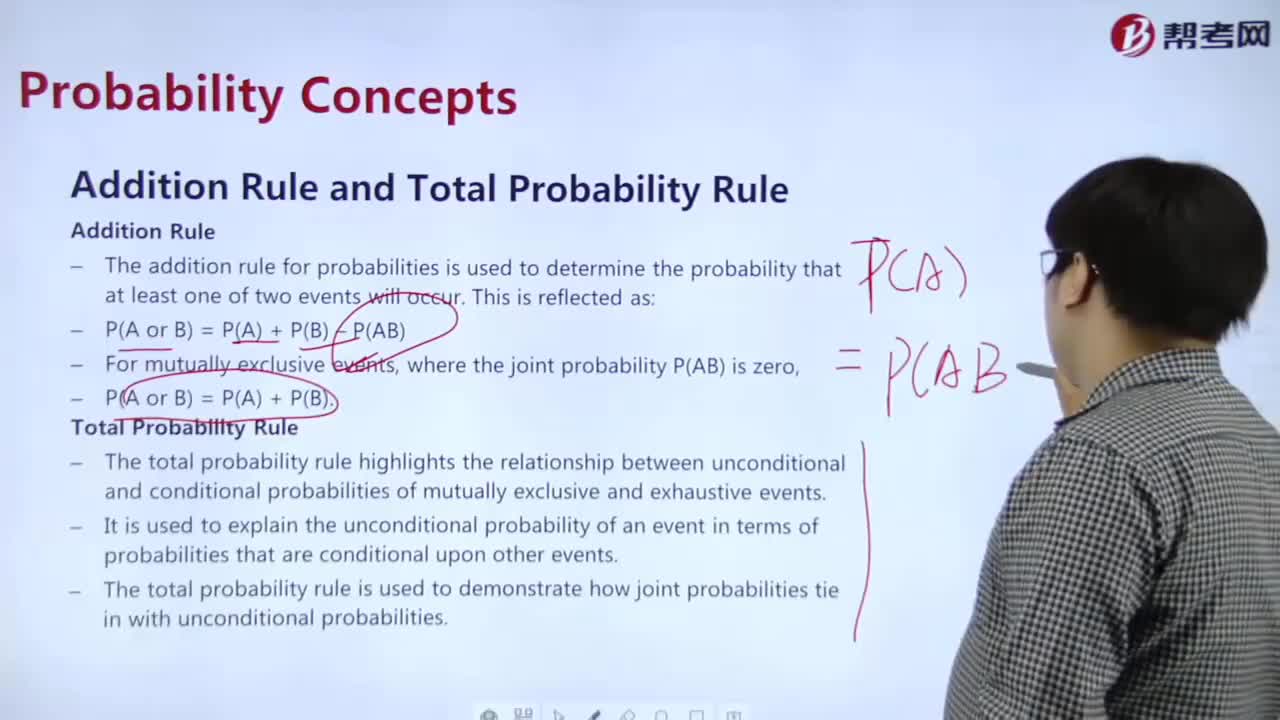
How to understand the addition rule and the total probability rule?

What is probability distribution?

What are the methods of share repurchase?

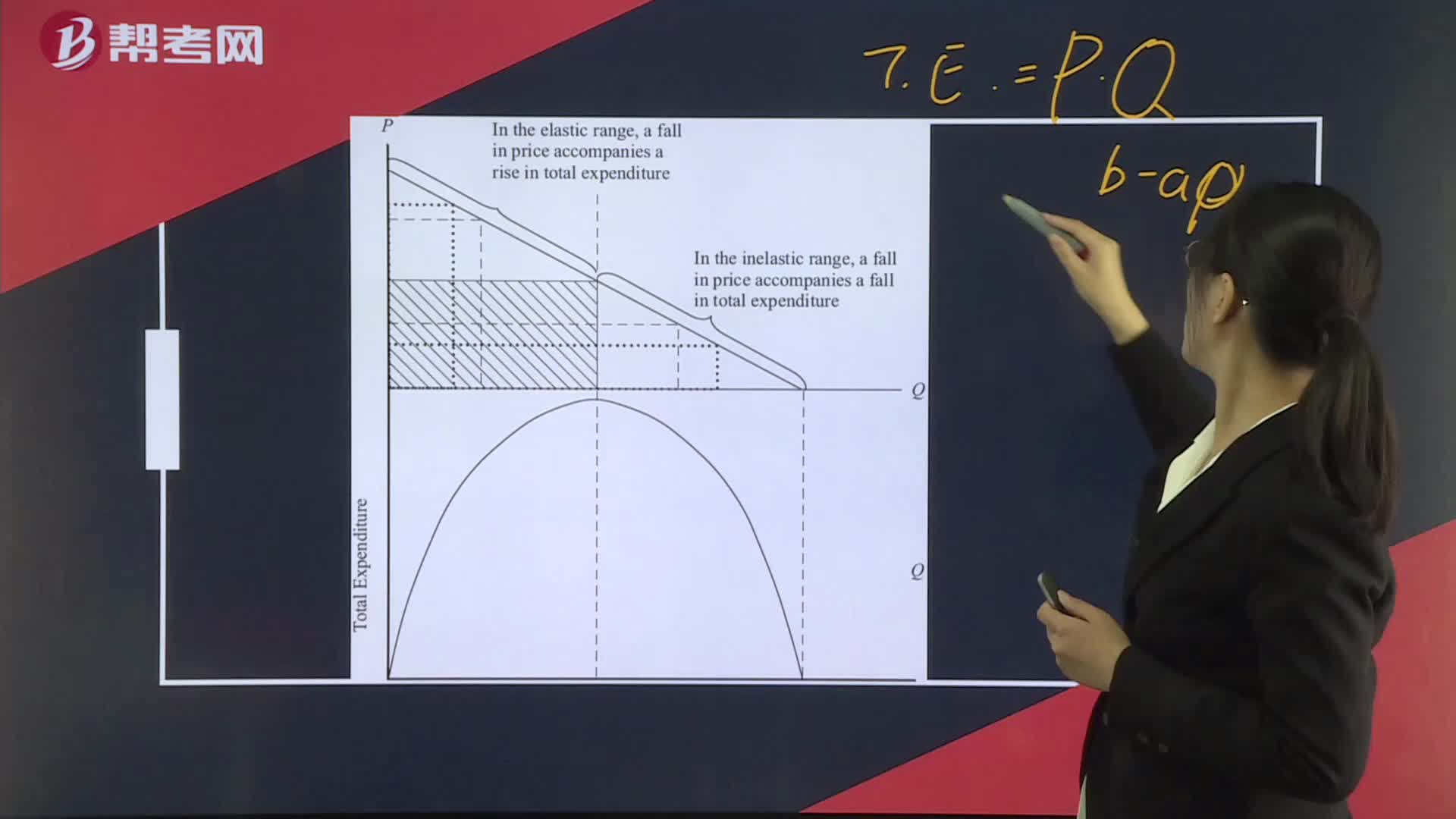
How To calculate total leverage?

What are the methods of dividend discount model?

What are the popular capital budgeting methods?

What are the methods of industrial analysis?

What are the investor's investment methods?

What are the weighting methods?

The Total Probability Rule

Probability Stated as Odds

Fundamental Concepts of Statistics

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360