
下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失
Probability
Random variable: a quantity whose outcomes (possible values) are uncertain. (eg. return on a risky asset)
An event is a specified set of outcomes.
Probability:
1 The probability of any event E is a number between 0 and 1: 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1.
2 The sum of the probabilities of any set of mutually exclusive and exhaustive events equals 1.Mutually exclusive means that only one event can occur at a time; exhaustive means that the events cover all possible outcomes.
Objective probability: Empirical and Priori
Empirical probability estimates the probability of an event as a relative frequency of occurrence based on historical data. Relationships must be stable through time for empirical probabilities to be accurate.
Priori probability: deduce probabilities by reasoning about the problem. based on logical analysis rather than on observation or personal judgment.
Subjective probability draws on personal or subjective judgment.
Probability Stated as Odds.
Given a probability P(E),
Odds for E = P(E)/[1 − P(E)].
Given odds for E of “a to b,” the implied P(E) is a/(a + b).
Odds against E = [1 − P(E)]/P(E)
Given odds against E of “a to b,” the implied P(E) is b/(a + b).
If P(E) = 1/8, the odds for E are (1/8)/(7/8) = (1/8)(8/7) = 1/7, or “1 to 7.”
In wagering, for odds of “15 to 1” against E a $1 wager on E, if successful, returns $15 in profits plus the $1 staked in the wager. We can calculate the bet’s anticipated profit as follows:
Win: Probability = 1/16; Profit =$15
Loss: Probability = 15/16; Profit =–$1
Anticipated profit = (1/16)($15) + (15/16)(–$1) = $0
[PRACTICE PROBLEMS] If the probability that Zolaf Company sales exceed last year’s sales is 0.167, the odds for exceeding sales are closest to:
A. 1 to 5.
B. 1 to 6.
C. 5 to 1.
[Solutions] A
Given odds for E of a to b, the implied probability of E = a/(a + b).
Stated in terms of odds a to b with a = 1, b = 5, the probability of E = 1/(1 + 5) = 1/6 = 0.167. This result confirms that a probability of 0.167 for beating sales is odds of 1 to 5.
Unconditional probability (marginal probability): the probability of this event A, P(A)
Conditional probability: the probability of A, given that B has occurred, P(A | B)
Joint probability: the probability of both A and B happening, P(AB)
Conditional Probability
P(A | B) = P(AB)/P(B), P(B) ≠ 0
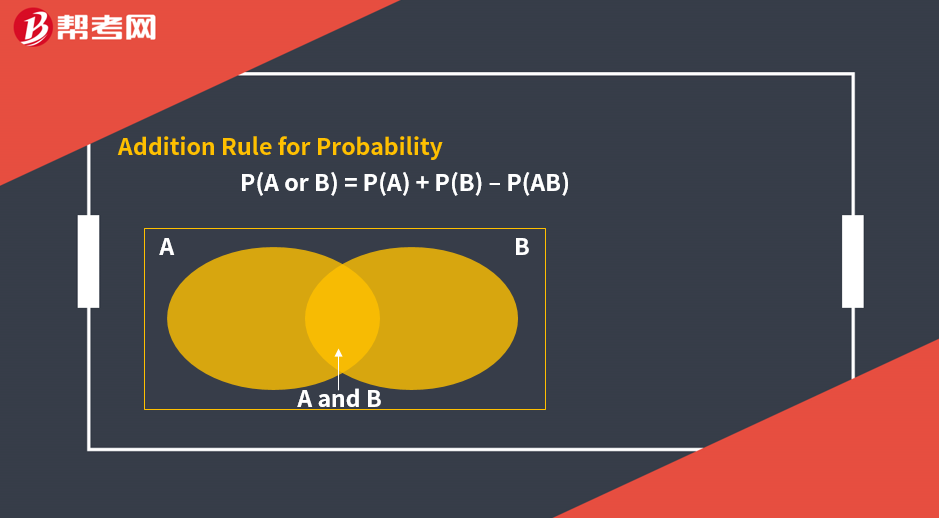
Multiplication Rule for Probability
P(AB) = P(A | B)P(B)
Independent Events: Two events A and B are independent if and only if P(A | B) = P(A) or, equivalently, P(B | A) = P(B).
Dependent Events: The probability of occurrence of one is related to the occurrence of the other.
Multiplication Rule for Independent Events:
P(AB) = P(A)P(B)
If we have an event or scenario S, the event not-S, called the complement of S, is written SC. P(S) + P(SC) = 1

[PRACTICE PROBLEMS] After estimating the probability that an investment manager will exceed his benchmark return in each of the next two quarters, an analyst wants to forecast the probability that the investment manager will exceed his benchmark return over the two-quarter period in total. Assuming that each quarter’s performance is independent of the other, which probability rule should the analyst select?
A. Addition rule
B. Multiplication rule
C. Total probability rule
[Solutions] B
Because the events are independent, the multiplication rule is most appropriate for forecasting their joint probability. The multiplication rule for independent events states that the joint probability of both A and B occurring is P(AB) = P(A)P(B).
 208
208The Total Probability Rule:not-S,the two-quarter period in total.rulejoint probability of both A and B occurring is PAB = PAPB.
 168
168Probability:Random:variable:a quantity whose outcomes possible values;An event is a specified set of outcomes.:timeObjectiveprobability draws on personal or subjective judgment.
 214
214Probability Stated as Odds:Odds against E = [1 − PE]PE,if:successful;calculate the bet’s anticipated profit as follows:Win,Lossprobability of 0.167 for beating sales is odds of 1 to 5.

微信扫码关注公众号
获取更多考试热门资料