
下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失
Supply Analysis:The Firm
Increasing marginalreturns: marginal product increases as additional units of that input are employed.
Initially, a firm can experience increasing returns from adding labor to the production process. But after a certain output level, the law of diminishingmarginal returns becomes evident.

Marginal returns are directly related to inputproductivity, a measure of the output per unit of input.
The total cost of production (TC):
TC = (w)(L) + (r)(K)
Two things could cause the cost of producing any given level of output to fall:
Either the price of one or both inputs could fall or the inputs themselves could become moreproductive and less of them would be needed
Total product (Q)
The aggregate sum of production for a firm during a time period. Usually illustrated as the total output (Q) using labor quantity (L)
Average product
Total product divided by the quantity of a given input. (APL = Q/L)
Marginal product
The amount of additional output resulting from using one more unit of input assuming other inputs are fixed. (MPL = ΔQ/ΔL)
[Practice Problems] The manager of a small manufacturing firm gathers the following information about the firm’s labor utilization and production:
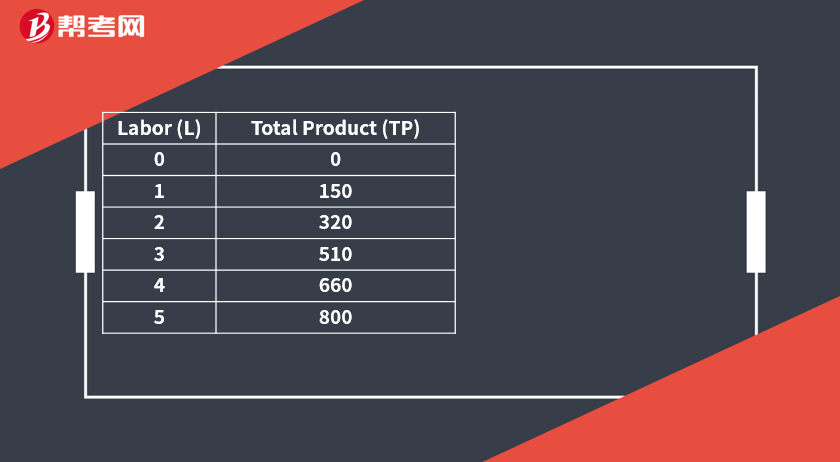
[Practice Problems] Refer to the data in the exhibit. The number of workers resulting in the highest level of average product of labor is closest to:
A. 3.
B. 4.
C. 5.
[Solutions] A
Three workers produce the highest average product equal to 170.
AP = 510/3 = 170.
[Practice Problems] Refer to the data in the exhibit. The marginal product of labor demonstrates increasing returns for the firm if the number of workers is closest to but not more than:
A. 2.
B. 3.
C. 4.
[Solutions] B
Marginal product is equal to the change in total product divided by the change in labor. The increase in MP from 2 to 3 workers is 190:
MP = ΔTP/ΔL = (510 – 320)/(3 – 2) = 190/1 = 190.
Economic profit is defined as the difference between total revenue (TR) and total economic costs.
Accounting profit is the difference between TR and total accounting cost.
Normal profit is the level of accounting profit such that economic profit is zero.
Economic costs are the sum of total accounting costs and implicit opportunity costs.
The labor expense is both an economic cost and an accounting cost.
Economic depreciation is forward looking.
Accounting depreciation is backward looking.
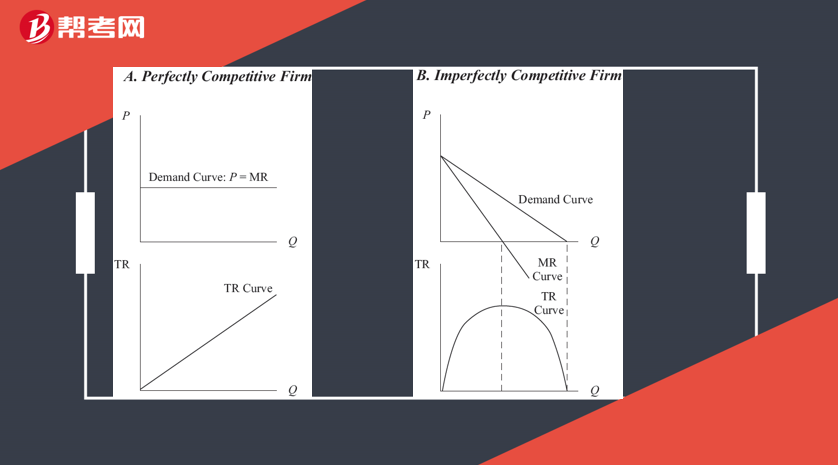
Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue the firm realizes from the decision to increase output by one unit per time period.
MR = ΔTR/ΔQ.
In a perfectly competitive market, MR = P.
Under imperfect competition, MR < P.
[Practice Problems] The marketing director for a Swiss specialty equipment manufacturer estimates the firm can sell 200 units and earn total revenue of CHF500,000. However, if 250 units are sold, revenue will total CHF600,000. The marginal revenue per unit associated with marketing 250 units instead of 200 units is closest to:
A. CHF 2,000. B. CHF 2,400. C. CHF 2,500.
[Solutions] A
Marginal revenue per unit is defined as the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity sold. MR = ΔTR ÷ ΔQ. In this case, change in total revenue equals CHF100,000, and change in total units sold equals 50.
CHF100,000 ÷ 50 = CHF2,000.
Marginal cost (MC) is the increase to total cost resulting from the firm’s decision to increase output by one additional unit per time period.
MC = ΔTC/ΔQ.
Short-run marginal cost (SMC) is the additional cost of the variable input, labor, that must be incurred to increase the level of output by one unit. SMC = w/MPL.
Long-run marginalcost (LMC) is the additional cost of all inputs necessary to increase the level of output, allowing the firm the flexibility of changing both labor and capital inputs in a way that maximizes efficiency.
Variable costs are all costs that fluctuate with the level of production and sales.
Average variable cost (AVC) is the ratio of total variable cost to total output: AVC = TVC/Q.
AVC = w/APL
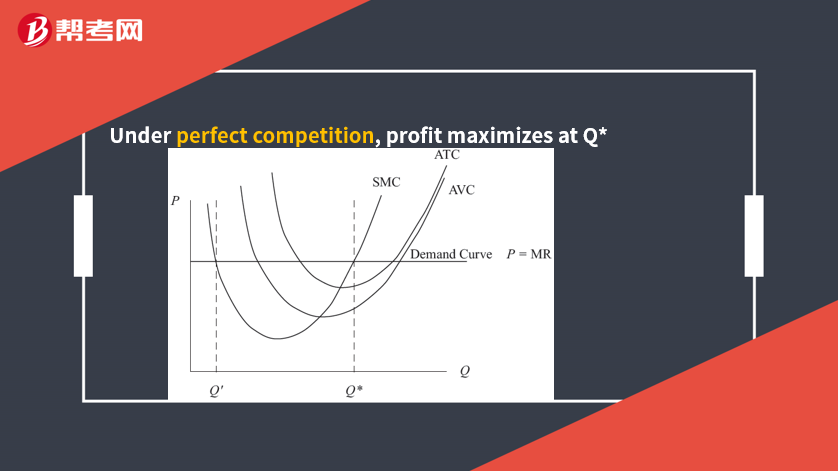
The profit-maximization decision for an operating firm as follows: Produce the level of output such that (1) MR = MC and (2) MC is not falling.
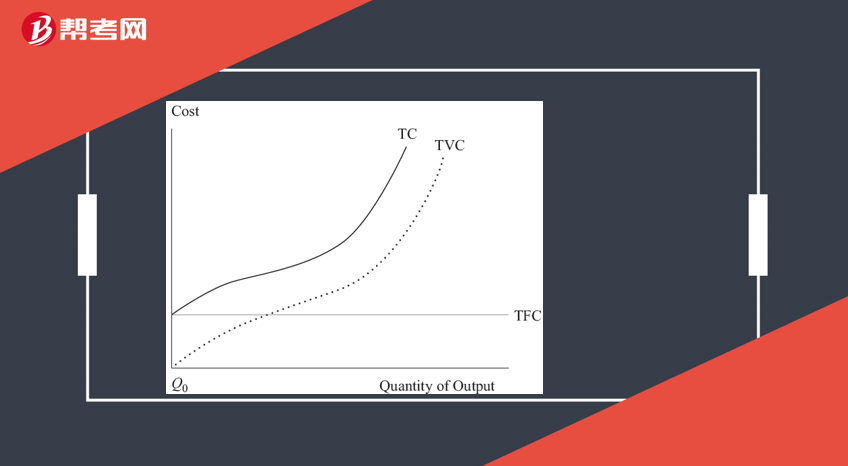
TC is the summation of all costs, where costs are classified on the basis of whether they are fixed or variable.
Total fixed cost (TFC) is the summation of all expenses that do not change as the level of production varies.
Total variable cost (TVC) is the summation of all variable expenses.
[Practice Problems] A firm’s director of operations gathers the following information about the firm’s cost structure at different levels of output:
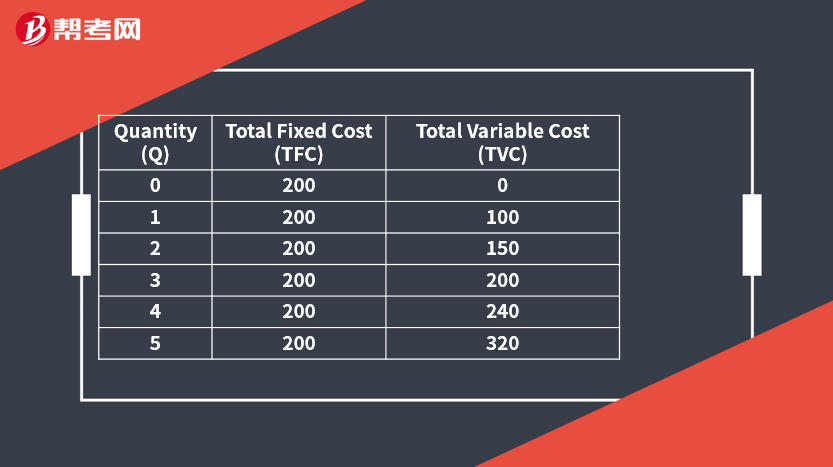
[Practice Problems] Refer to the data in the exhibit. When quantity produced is equal to 4 units, the average fixed cost (AFC) is closest to:
A. 50.
B. 60.
C. 110.
[Solutions] A
Average fixed cost is equal to total fixed cost divided by quantity produced: AFC = TFC/Q = 200/4 = 50.
[Practice Problems] Refer to the data in the exhibit. When the firm increases production from 4 to 5 units, the marginal cost (MC) is closest to:
A. 40.
B. 64.
C. 80.
[Solutions] C
Marginal cost is equal to the change in total cost divided by the change in quantity produced. MC = ΔTC/ΔQ = 80/1 = 80.
[Practice Problems] Refer to the data in the exhibit. The level of unit production resulting in the lowest
average total cost (ATC) is closest to:
A. 3.
B. 4.
C. 5.
[Solutions] C
Average total cost is equal to total cost divided by quantity produced.
At 5 units produced the average total cost is 104. ATC = TC/Q = 520/5 = 104.
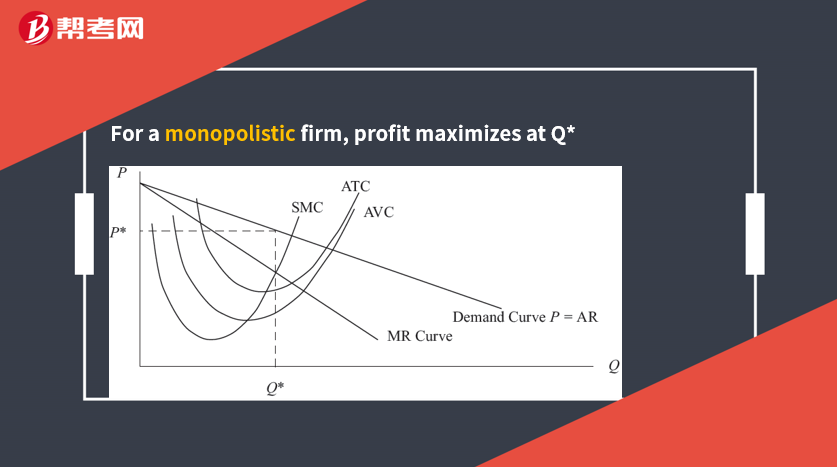
[Practice Problems] A profit maximum is least likely to occur when:
A. average total cost is minimized.
B. marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C. the difference between total revenue and total cost is maximized.
[Solutions] A
The quantity at which average total cost is minimized does not necessarily correspond to a profit maximum.
A firm is break even if TR = TC (AR = ATC).
A firm whose revenue is equal to its economic costs is covering the opportunity cost of all of its factors of production, including capital.
Such a firm is earning normal profit, but not positive economic profit.
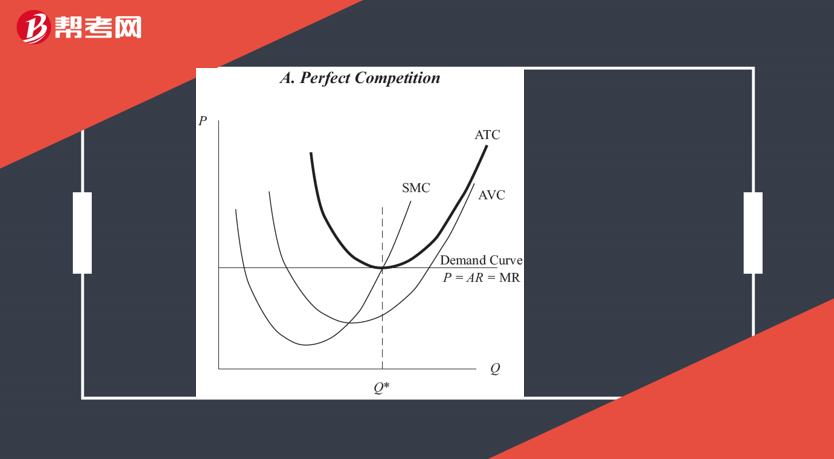
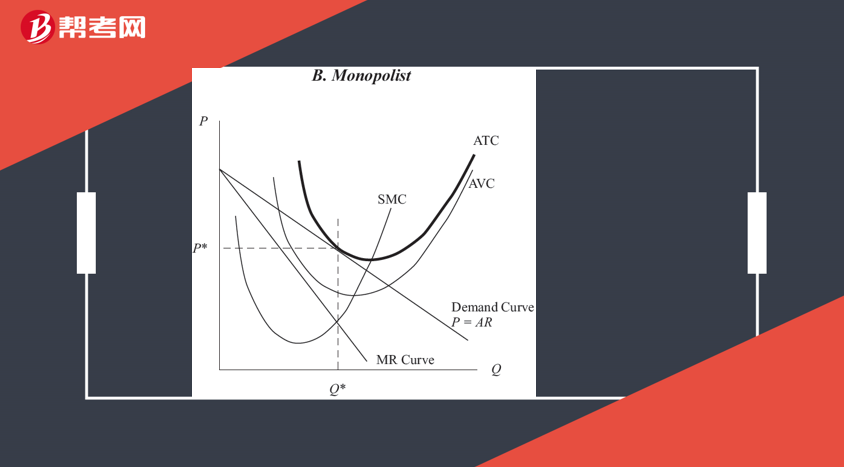
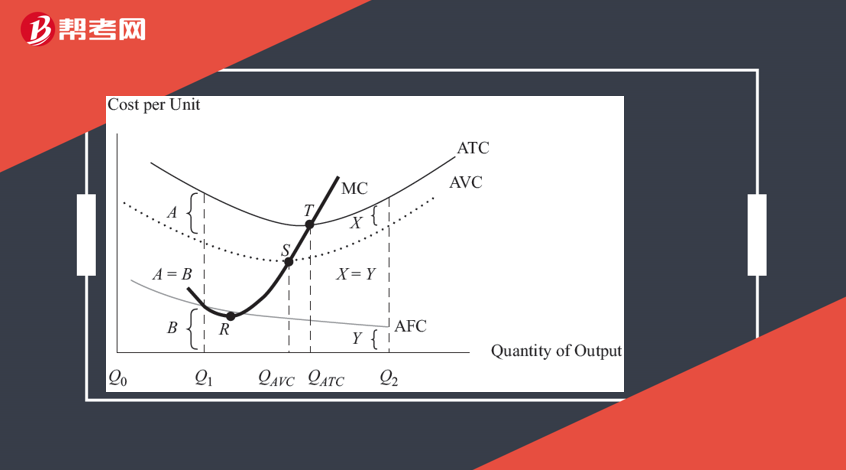
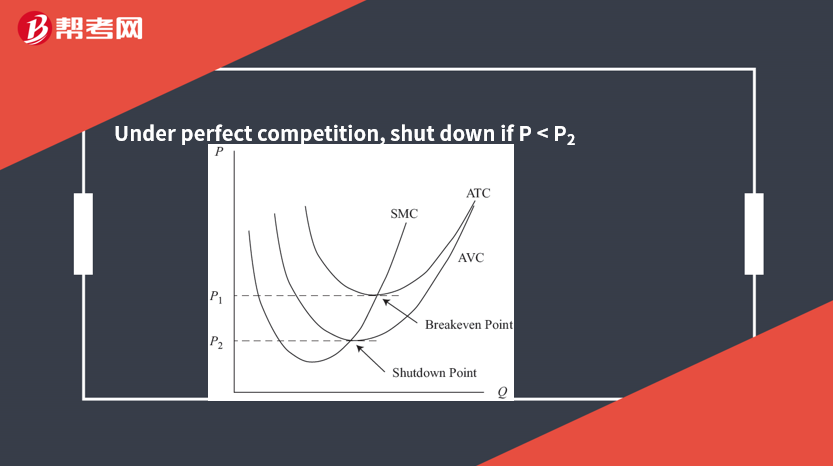
The shutdown point: the minimum AVC point
The breakeven poin: the minimum ATC point
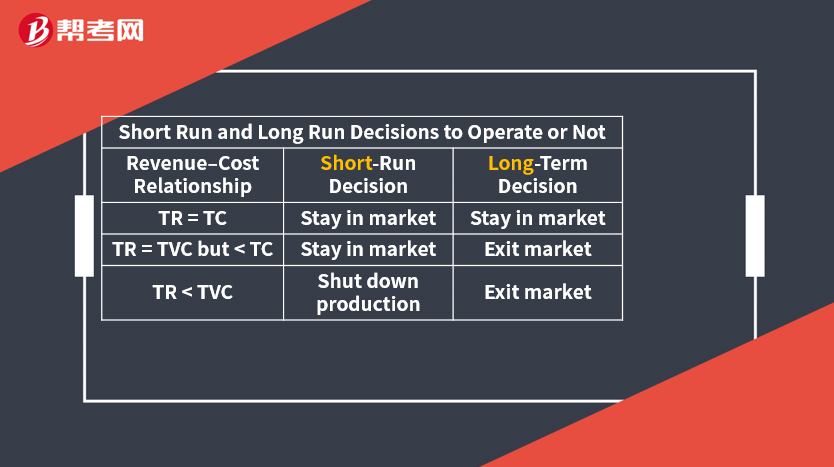
[Practice Problems] A company has total variable costs of $4 million and fixed costs of $3 million. Based on this information, the company will stay in the market in the long term if total revenue is at least:
A. $3.0 million.
B. $4.5 million.
C. $7.0 million.
[Solutions] C
A company will stay in the market in the long term if total revenue is equal to or greater than total cost. Because total costs are $7 million ($4 million variable costs and $3 million fixed costs), the company will stay in the market in the long term if total revenue equals at least $7 million.
Short- and Long-Run Cost Curves
At higher levels of fixed input, TFC is greater but the production capacity of the firm is also greater.
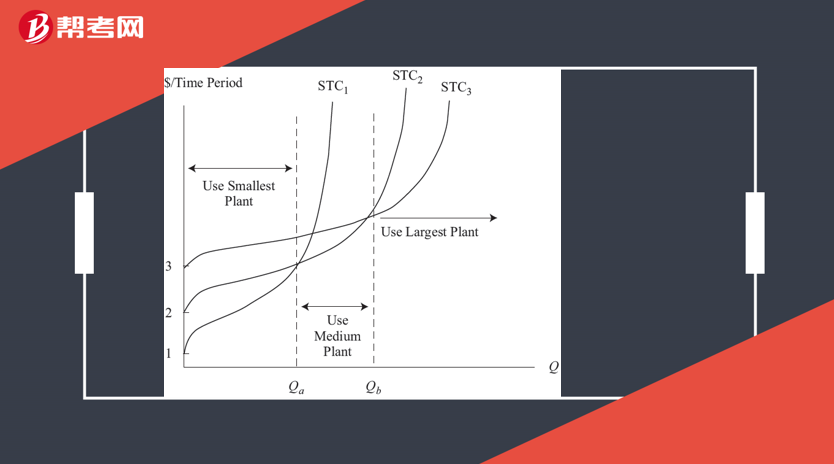
The long-run total cost curve is derived from the lowest level of STC for each level of output—an “envelope curve.”
For each STC curve, there is also a corresponding short-run average total cost (SATC) curve and a corresponding long-run average total cost (LRAC) curve.
Economies of scale occur if, as the firm increases its output, cost per unit of production falls.
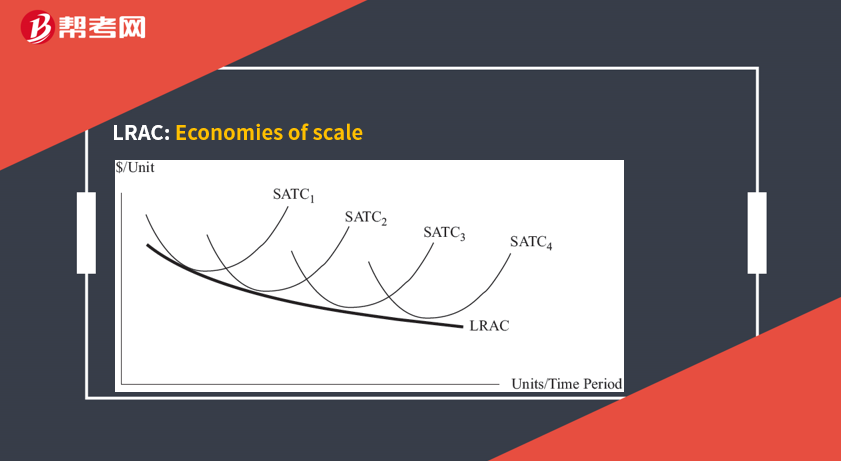
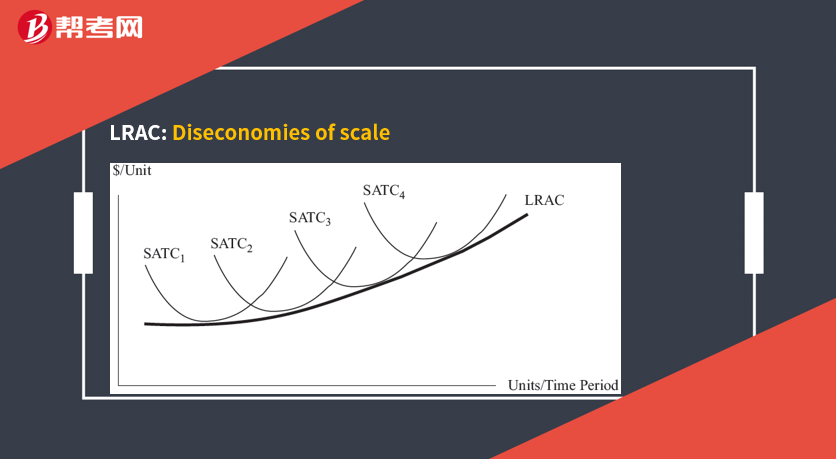
Diseconomies of scale occur if cost per unit rises as output increases.
Economies of scale can result from:
Increasing returns to scale.
Specialization economies.
Equipment and technology improvement.
Enhanced cost control and quality control.
More effective managerial decision making.
Bargaining power in input price.
Diseconomies of scale can result from:
Decreasing returns to scale.
Too large to be properly managed.
Overlapping and duplication products.
Higher prices because of supply constraints when buying inputs in large quantities.
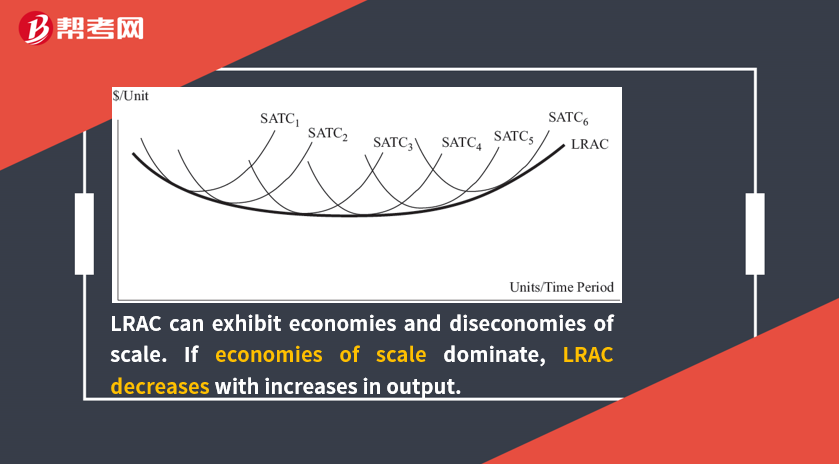
The minimum point on the LRAC curve is referred to as the minimum efficient scale.
The minimum efficient scale is the optimal firm size under perfect competition over the long run.
 184
184Supply Analysis:The Firm:units of that input are employed.:Initially:levelproductive and less of them would be needed
 160
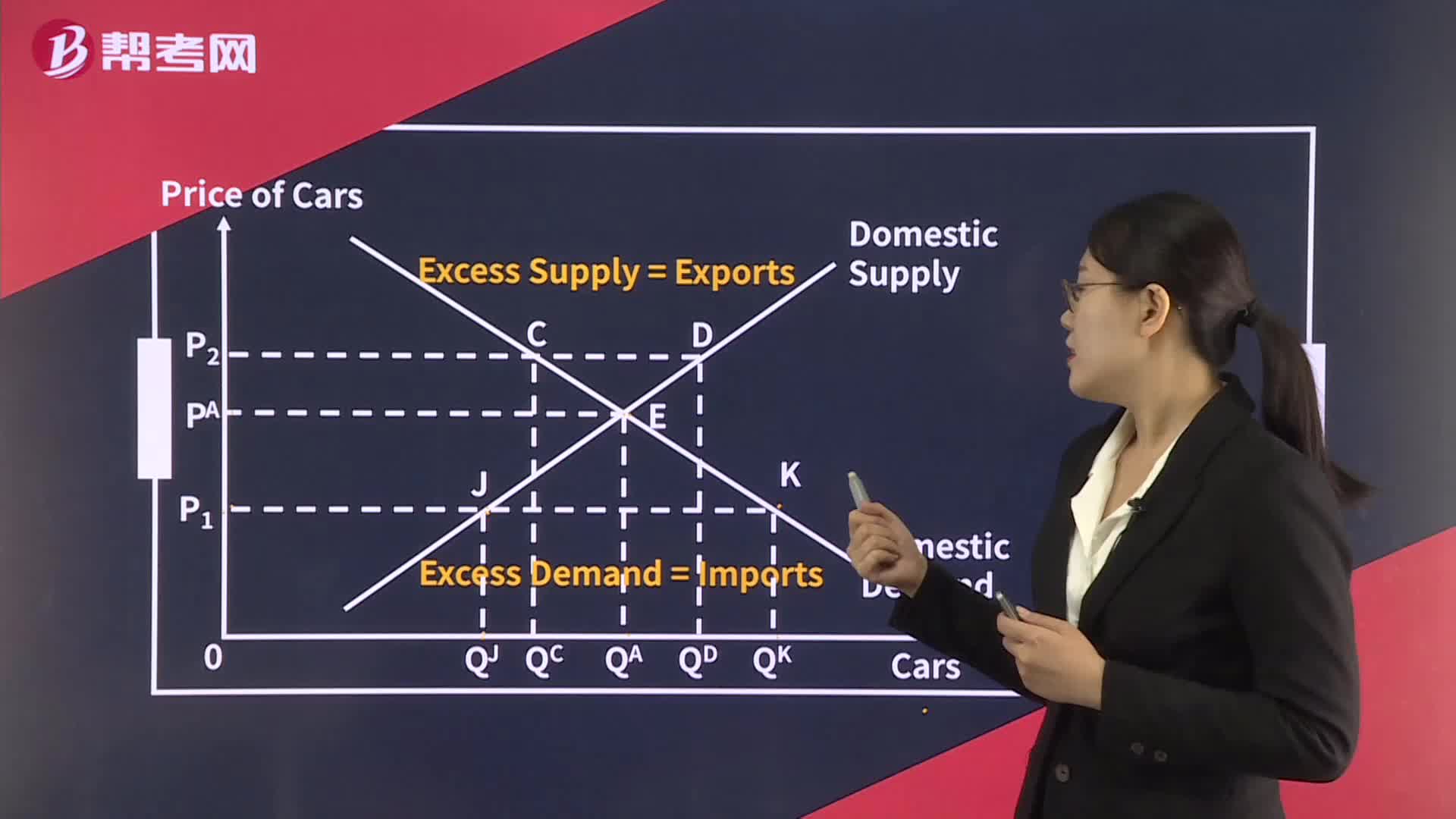
160Excess Demand, Excess Supply:Excess Supply
 195
195The Supply and Demand for Money:Interest”rates effectively adjust to bring the market into:Moneythat the money supply can affect real things in the short run.

微信扫码关注公众号
获取更多考试热门资料