
下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失

请谨慎保管和记忆你的密码,以免泄露和丢失
Fiscal Policy and Aggregate Demand
A primary aim for fiscal policy is to help manage the economy through its influence on aggregate national output, real GDP.

An expansionary policy could take one or more of the following forms:
Cuts in personal income tax raise disposable income, boosting aggregate demand.
Cuts in sales (indirect) taxes to lower prices, raises real incomes, raising consumer demand.
Cuts in corporation (company) taxes to boost business profits, raise capital spending.
Cuts in tax rates on personal savings to raise disposable income, raising consumer demand.
New public spending on social goods and infrastructure, boosting personal incomes, raising aggregate demand.
Keynesians believe that fiscal policy can have powerful effects on aggregate demand, output, and employment when there is substantial spare capacity in an economy.
Monetarists believe that fiscal changes only have a temporary effect on aggregate demand and that monetary policy is a more effective tool for restraining or boosting inflationary pressures. Monetarists tend not to advocate using monetary policy for countercyclical adjustment of aggregate demand.
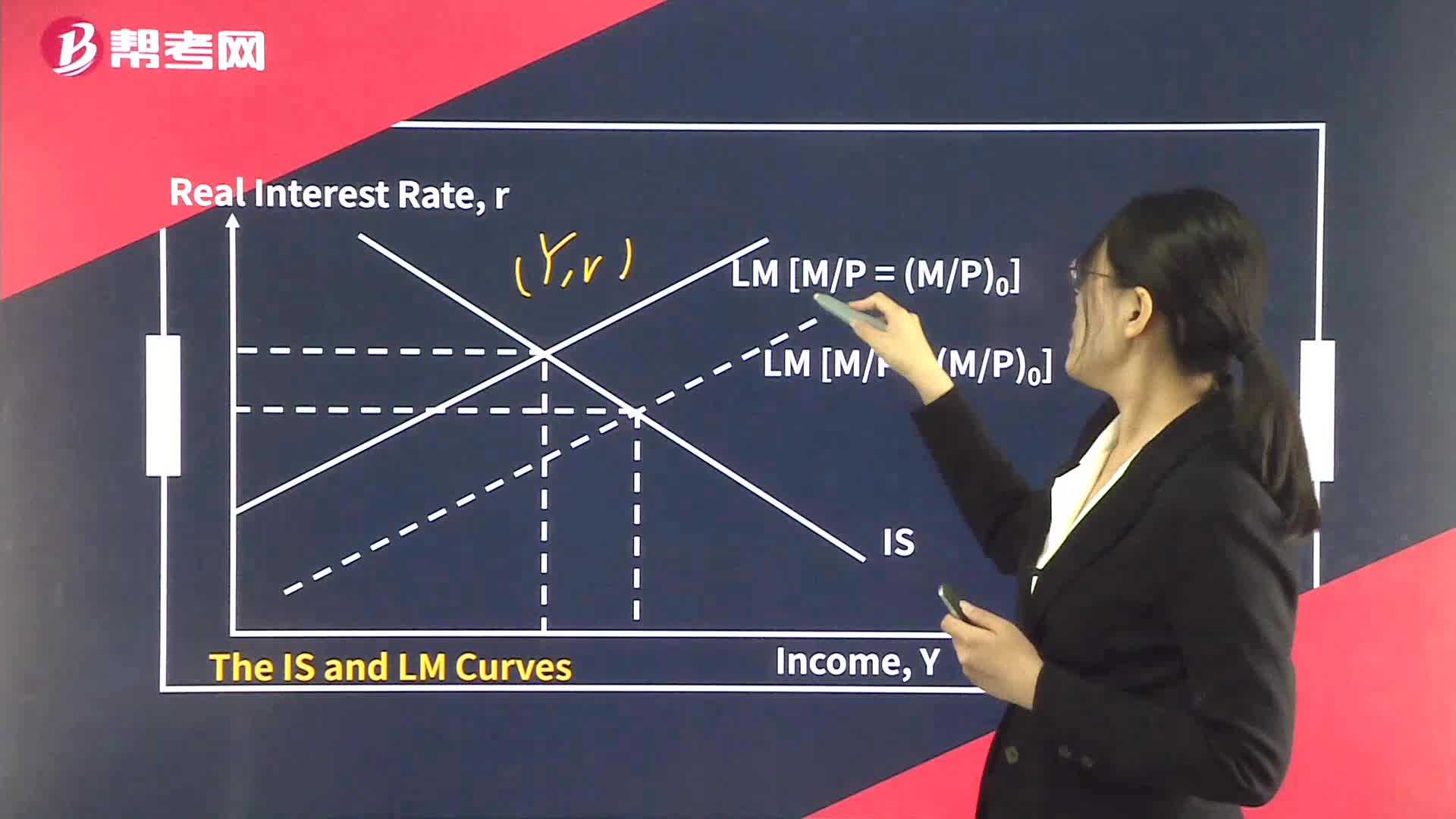 354
354The Aggregate Demand Curve:changes in private saving S.;money demand is insensitive to Y.
 73
73Shifts in Aggregate Demand and Supply:economy associated with the business cycle.
 176
176The Relationship Between Fiscal and Monetary Policy:Policyassumption is made that wages and prices are rigid

微信扫码关注公众号
获取更多考试热门资料