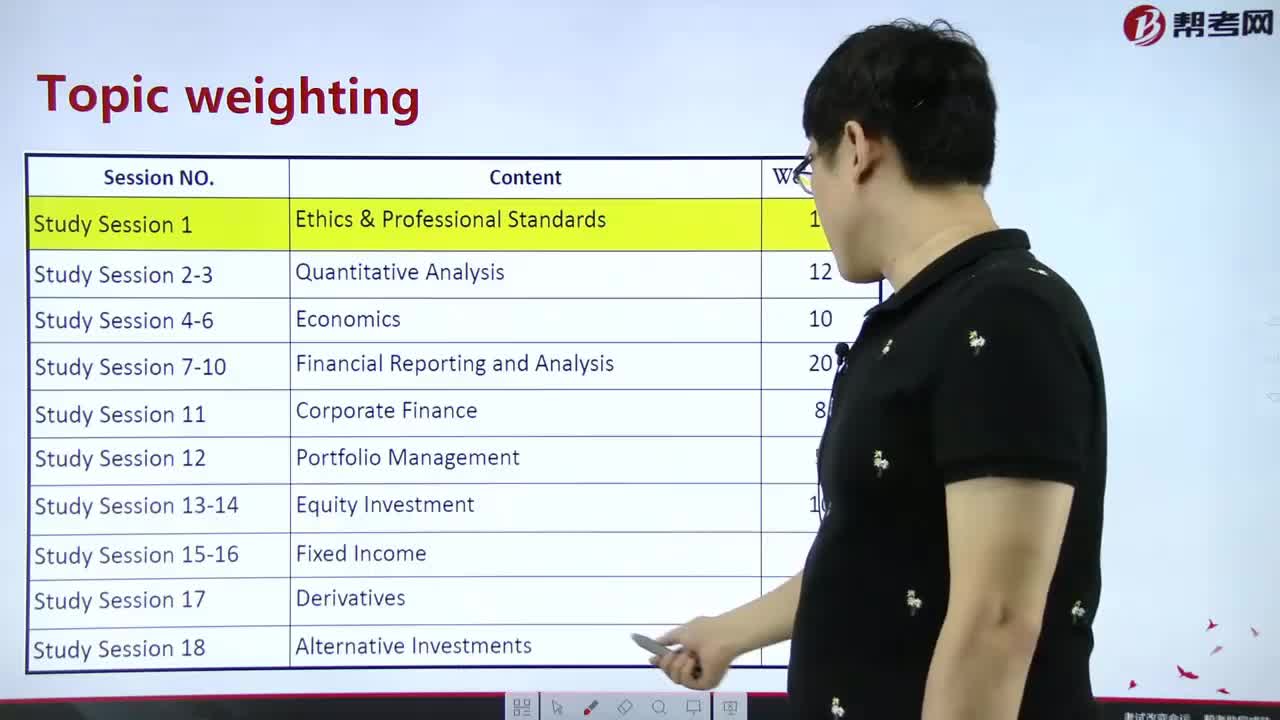
Long-Run Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition

Kinked Demand Curve in Oligopoly Market

Shifts in Aggregate Demand

Equilibrium GDP and Prices – Stagflation

Shifts in Aggregate Demand and Supply

Equilibrium GDP and Prices

Factors Affecting Long-Run Equilibrium in Monopoly Markets

Demand Analysis in Perfect Competition
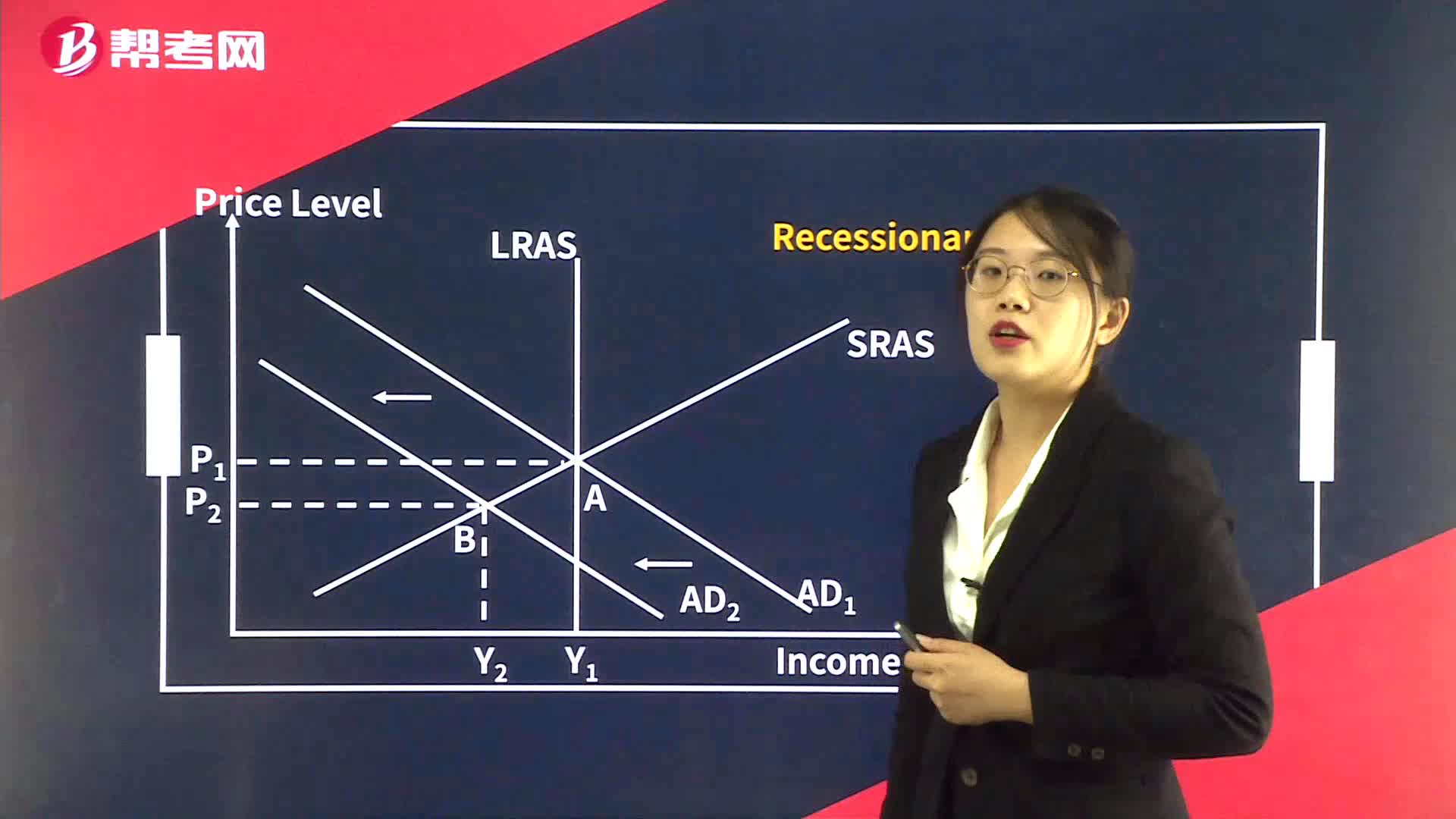
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Recessionary Gap
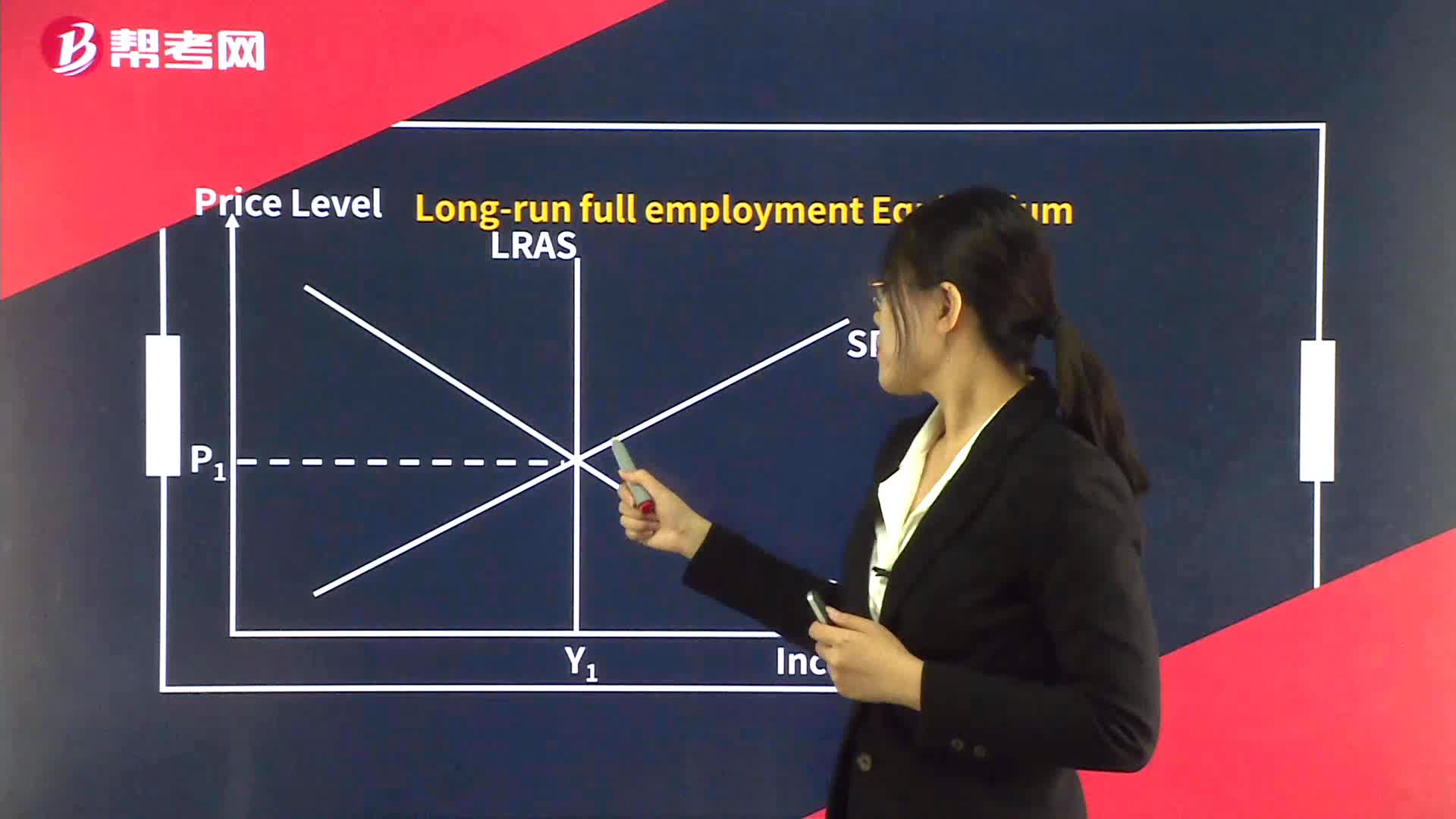
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Long-Run Equilibrium
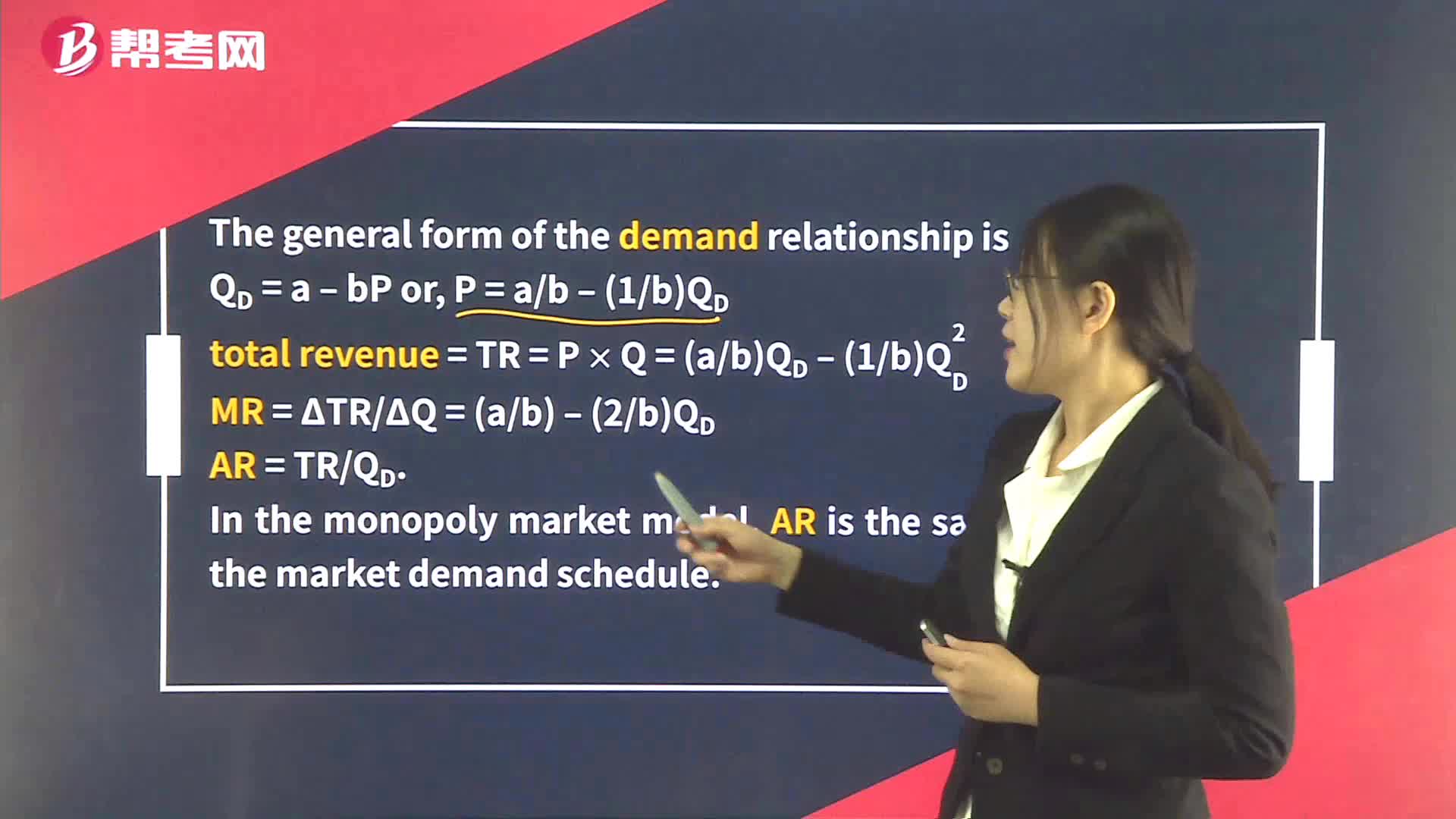
Demand Analysis in Monopoly

Difficulties in Executing Fiscal Policy

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360