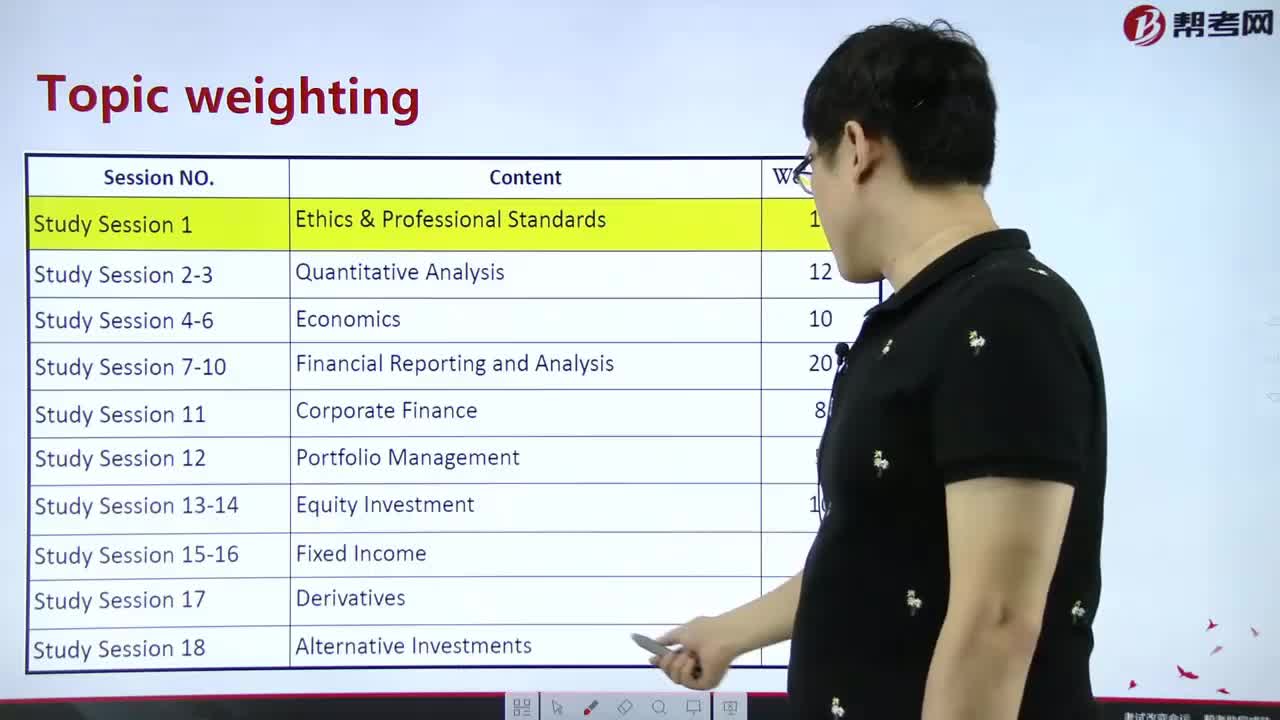
Theories of the Business Cycle - Monetarist School

Theories of the Business Cycle - Keynesian School

The New Classical School

Resource Use through the Business Cycle

Resource Use through the Business Cycle - Inventory

Resource Use through the Business Cycle - Consumer Behavior
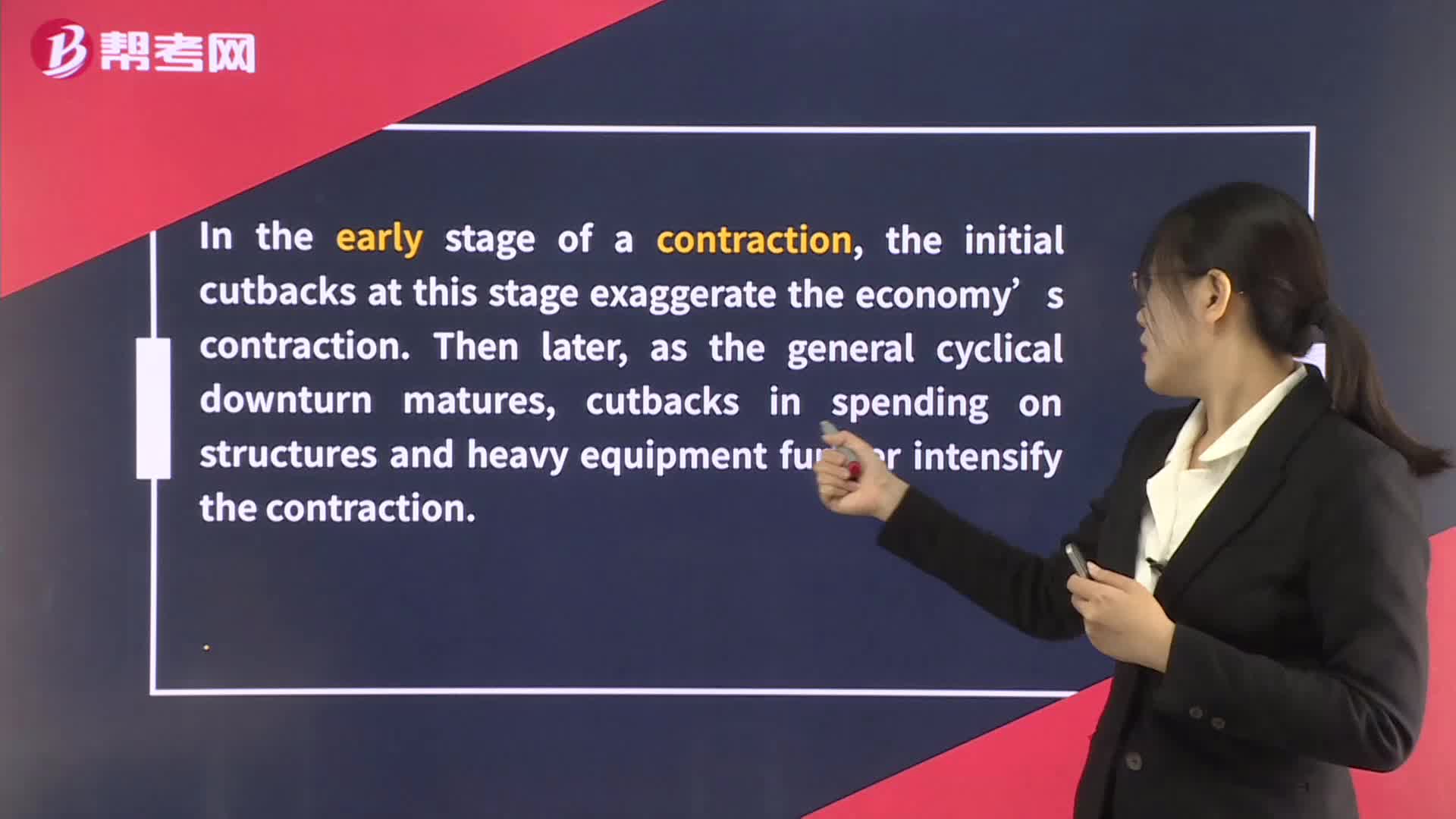
Resource Use through the Business Cycle - Capital Spending

Phases Of the Business Cycle

Housing Sector Behavior through the Business Cycle

Measures of Central Tendency

External Trade Sector Behavior through the Business Cycle
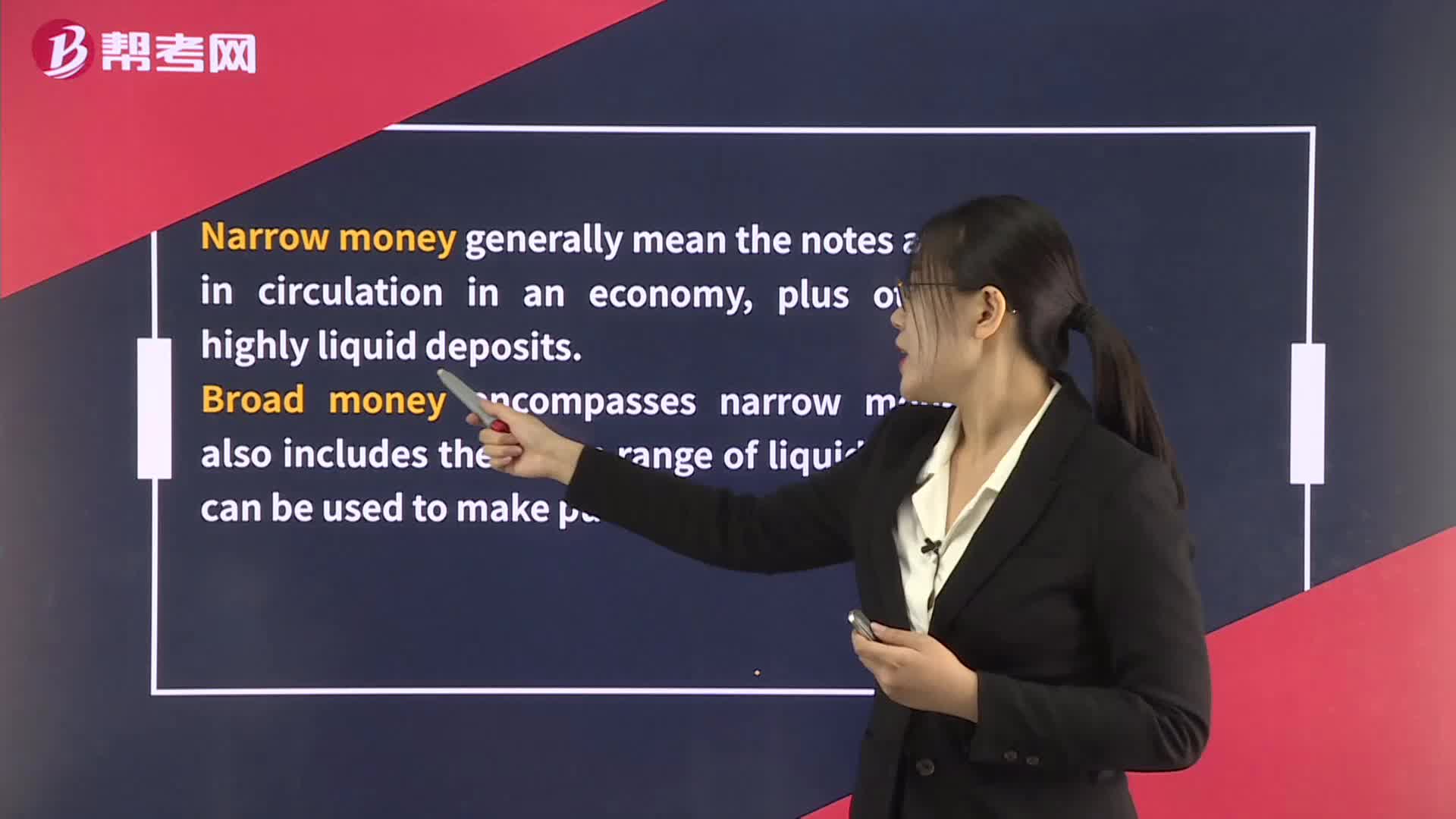
Definitions of Money

下载亿题库APP
联系电话:400-660-1360